Imagine a world where your medical history is as easy to access as your favorite playlist—any doctor, anywhere, can see the complete picture of your health in seconds. Sounds ideal, right? This is exactly what interoperable health records aim to achieve today.
At its heart, interoperability is about breaking down silos, helping different systems to speak the same language, and turning fragmented data into actionable insights. It’s a game-changer for how care is delivered—making it faster, smarter, and more centered around the patient.
But why is this seamless exchange of information such a big deal? Let’s explore:
Table of Contents
The Pillars of Interoperability in Healthcare
Healthcare systems are intricate and multifaceted. Hospitals, clinics, diagnostic labs, pharmacies, and insurance providers all generate vast amounts of data daily. However, this data often exists in silos, locked within proprietary systems that don’t communicate with one another. By bridging these silos, interoperability facilitates the seamless exchange of information across various platforms and stakeholders.
1. Improving Patient Care
When healthcare providers have immediate access to a patient’s complete medical history, including past diagnoses, medications, and test results, it reduces the likelihood of errors. For example:
- Physicians can avoid prescribing medications that might interact with a patient’s existing drugs.
- Diagnostic tests are less likely to be duplicated.
- Emergency care becomes more precise, with real-time access to critical data.
2. Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Interoperability isn’t just about patient care; it also streamlines administrative processes. Consider the vast amount of paperwork involved in insurance claims or the logistical nightmare of coordinating care among multiple providers. Seamless data-sharing reduces redundancies, automates routine tasks, and speeds up decision-making processes, ultimately lowering costs.
3. Empowering Patients
Patients are increasingly taking control of their health journeys. Through interoperable systems, they can access their health records, track treatment progress, and even share data from wearable devices with their physicians. This transparency fosters trust and engagement, which helps patients make informed decisions.
The Role of Seamless Data-Sharing
At the heart of interoperability lies seamless data-sharing—the ability to exchange information in a standardized, meaningful way. However, achieving this is easier said than done. Healthcare systems often use different data formats, communication protocols, and terminologies, which creates barriers to interoperability.
Breaking Down Barriers to Interoperability
Interoperability doesn’t happen by accident—it requires deliberate strategies to create systems that “speak the same language.” Here’s how key components come into play:
1. Standardization as a Foundation
Frameworks like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) are universal translators for disparate systems. They standardize data structure and communication, thus facilitating seamless exchange of patient records, lab results, and treatment plans. Standardization eliminates guesswork, reduces errors, and improves clarity across platforms, much like a common dictionary in a multilingual conversation.
2. Data Transformation
Even with standardized frameworks, healthcare data often originates from legacy systems that don’t conform to modern standards. This is where data transformation plays a key role. For example, a lab result stored in an outdated system might need to be translated into a FHIR-compliant format to integrate with an advanced electronic health record (EHR) system. These conversions, often carried out in real-time, smooth out the rough edges of data sharing.
3. APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) act as connective tissues in healthcare interoperability. They allow systems to interact with each other by providing a bridge for data to move back and forth securely and efficiently. APIs built on modern standards like FHIR take this connectivity further by facilitating real-time interactions. For example, when a clinician requests a patient’s lab results, an API can instantly retrieve and display the data.
How AERIS Facilitates Interoperability with Real-Time Data Exchange
In healthcare, data is generated in various formats—HL7 messages, FHIR resources, XML structures, JSON payloads, nested relational databases, flat file structures, etc. These diverse formats pose a challenge for seamless data exchange between systems like electronic health records (EHRs), diagnostic labs, and insurance portals. However, AERIS acts as a universal translator that facilitates real-time data exchange across all healthcare stakeholders.
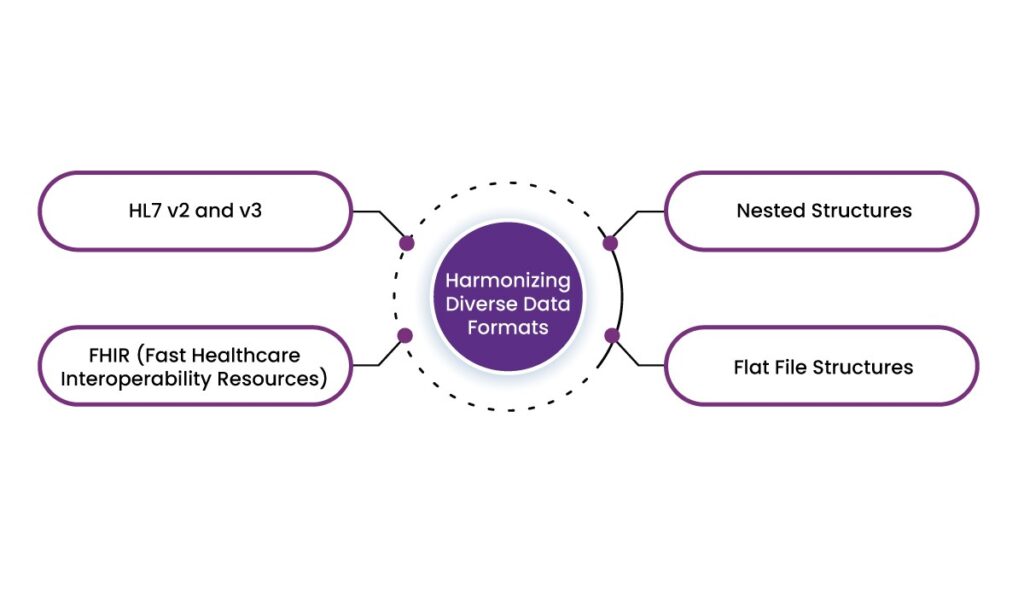
1. Harmonizing Diverse Data Formats
Healthcare data does not follow a one-size-fits-all format. For example:
- HL7 v2 and v3: Often used in hospitals for lab orders, radiology results, or admission details.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): Increasingly adopted for mobile applications, cloud communications, and modern EHRs.
- Nested Structures: Common in hierarchical databases, storing complex clinical data such as multi-step lab processes or nested test results.
- Flat File Structures: Widely used in legacy systems for tabular data like billing and claims.
AERIS simplifies the complexities of these disparate formats by automatically converting them into a standardized structure. For example, if a diagnostic lab generates a nested XML report containing patient test results, AERIS can translate this data into the FHIR-compliant JSON format if required.
2. Adding Value Beyond Data Translation
What sets AERIS apart is its ability to add contextual insights during translation. For example, when converting nested clinical data into FHIR, AERIS can also validate it against healthcare regulations and flag inconsistencies. This facilitates not only smooth data exchange but also enhances data integrity and compliance with standards.
Final Thoughts
Today, the importance of interoperability cannot be overstated. By breaking down barriers between systems, it paves the way for better patient outcomes, streamlined operations, and empowered individuals. Thus, the future of healthcare lies in seamless, efficient, and standardized data sharing—and it starts with adopting the right solutions.
Empower Your Healthcare System with AERIS
AERIS goes beyond standard interoperability solutions, offering real-time data exchange and advanced standardization that improve both operations and compliance. Whether you’re managing patient records, lab data, or insurance claims, AERIS ensures your systems work harmoniously to deliver optimal results.
Discover how AERIS can transform your healthcare operations and redefine the way you deliver care. Contact us today and step into the future of connected healthcare.
FAQs
1. How does interoperability improve patient care?
Interoperability allows healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, which helps reduce errors, avoid duplicate tests, and provide accurate emergency care.
2. What are the main barriers to interoperability in healthcare?
Common barriers include the use of proprietary systems, varying data formats, lack of standardized communication protocols, and legacy systems that are not compatible with modern frameworks.
3. What roles do standards like HL7 and FHIR play in healthcare interoperability?
HL7 and FHIR are standardized frameworks that enable different healthcare systems to communicate effectively by using a common structure and format for data exchange.
4. How does data transformation help achieve interoperability?
Data transformation converts information from legacy formats into standardized frameworks, making it compatible with modern systems. For example, AERIS can translate nested XML data into FHIR-compliant JSON format.
5. What are the benefits of interoperability for patients?
Patients gain access to their health records, can track treatment progress, and share data from wearable devices with healthcare providers, thus boosting engagement and better decision-making.
6. How does AERIS enhance healthcare interoperability?
AERIS simplifies real-time data exchange by harmonizing diverse data formats, adding contextual insights, and validating data for compliance, making systems work seamlessly together.
7. Why is real-time data exchange critical in healthcare?
Real-time data exchange enables faster decision-making, reduces administrative delays, and supports timely interventions, ultimately improving both patient outcomes and operational efficiency.













