Imagine rushing your loved one to the hospital in a critical emergency. The doctors are ready, the equipment is set, but suddenly, the system freezes. Patient records are inaccessible, billing transactions are halted, and chaos ensues. The culprit? A cyberattack that has locked the hospital out of its healthcare payment systems, demanding a ransom to regain access. This isn’t a scene from a dystopian thriller—it’s a growing reality in the healthcare industry.
With hospitals generating an astonishing 50 petabytes of data annually, the sector has become a prime target for cybercriminals. Every digital record holds sensitive patient information—names, medical histories, and financial details—making them invaluable on the black market. In fact, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recorded over 5,150 healthcare data breaches involving more than 500 records each between 2009 and 2022. In 2022 alone, cyberattacks in healthcare skyrocketed by 74%, with organizations facing an average of 1,463 attacks per week. The financial toll is staggering, with the average cost of a healthcare data breach reaching $10.93 million in 2023.
To combat this growing threat, healthcare institutions must rethink their approach to cybersecurity, especially in healthcare payment systems. By implementing multi-layered security protocols—strong encryption, identity verification, and strict access controls—hospitals can safeguard both patient data and financial transactions. But technology alone isn’t enough. Raising awareness among employees about phishing attacks and reinforcing cyber hygiene is just as crucial.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the importance of payment security to reduce fraud inthe healthcare industry.
Table of Contents
The Growing Threat of Fraud and Data Breaches in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations are particularly vulnerable to fraud and data breaches due to the high value of medical and financial data. Unlike other industries, stolen healthcare information can be used for various illicit activities, including identity theft, insurance fraud, and black-market sales. Some of the primary threats include:
- Medical Identity Theft: Fraudsters use stolen patient data to access medical services or file false insurance claims.
- Payment Fraud: Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in healthcare payment systems to carry out fraudulent transactions.
- Data Breaches: Cybercriminals target healthcare databases to steal large volumes of patient records.
- Ransomware Attacks: Malicious software encrypts healthcare data, demanding a ransom for its release.
With healthcare fraud costing billions of dollars annually, investing in robust payment security solutions is a necessity rather than a choice.
Understanding payment security measures in hospitals:
Hospitals handle vast amounts of sensitive financial and patient data, making them prime targets for fraud and cyberattacks. Hospitals implement advanced payment security measures such as encryption, tokenization, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and AI-driven fraud detection to prevent unauthorised access and data breaches.
For example, in 2021, Florida’s Broward Health suffered a cyberattack exposing the payment details of 1.3 million patients due to unauthorized access. To counter such threats, hospitals now rely on end-to-end encryption (E2EE) and tokenization, ensuring patient payment data is unreadable to hackers.
Another critical security measure is multi-factor authentication (MFA). Mayo Clinic, for instance, uses biometric authentication in its healthcare payment systems to verify users before processing transactions, reducing the risk of unauthorized payments.
AI-powered fraud detection is another key security measure. Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles leverages real-time monitoring and machine learning algorithms to flag suspicious transactions, helping to prevent fraudulent billing and identity theft.
By adopting these security measures, hospitals protect patient trust, ensure regulatory compliance (HIPAA & PCI DSS), and reduce financial losses from fraud. As cyber threats continue to evolve, robust payment security is no longer optional but a necessity for the healthcare industry.
Key Payment Security Measures to Reduce Fraud and Data Breaches
To combat these threats, healthcare organizations must implement stringent security measures. Paynova, a leader in secure digital payments, advocates for the following best practices:
1. Adopting End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) ensures that sensitive payment data is encrypted from the moment it is entered into the healthcare payment systems until it reaches its final destination. This prevents unauthorized access and interception by cybercriminals.
- Encrypts payment information before transmission.
- Protects data from being read or modified during transit.
- Reduces risk of financial and identity theft.
Paynova incorporates advanced encryption techniques into its healthcare payment systems, ensuring that all transactions remain secure and confidential.
2. Implementing Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with unique tokens that hold no intrinsic value. This prevents cybercriminals from accessing or using actual payment details, even if they infiltrate a healthcare provider’s system.
- Converts payment card details into randomized tokens.
- Ensures tokens are useless outside of the secure healthcare payment systems.
- Lowers the risk of data theft and fraud.

With tokenization, healthcare payment systems like Paynova enhance security for healthcare transactions while ensuring compliance with global standards like PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple authentication factors.
- Combines passwords with biometric scans, OTPs, or security tokens.
- Reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Strengthens protection for both patients and healthcare providers.
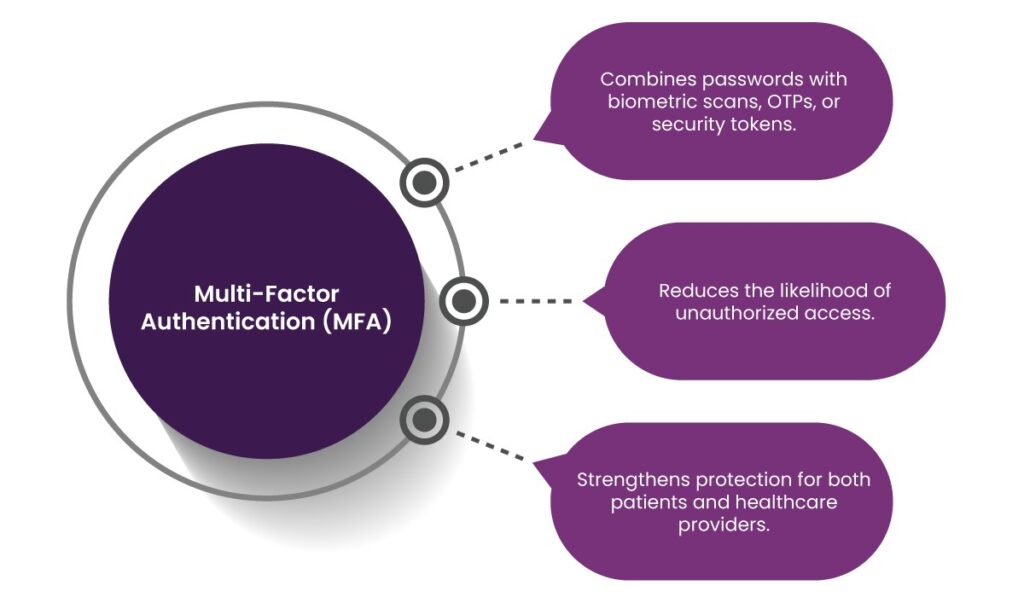
Paynova integrates MFA into its payment solutions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access or process transactions.
4. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Healthcare payment systems must comply with strict regulatory frameworks to ensure data security and prevent fraud. Some essential regulations include:
- PCI-DSS: Ensures secure payment processing by enforcing strong security controls.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Protects patient data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Governs the handling of personal data in healthcare transactions.
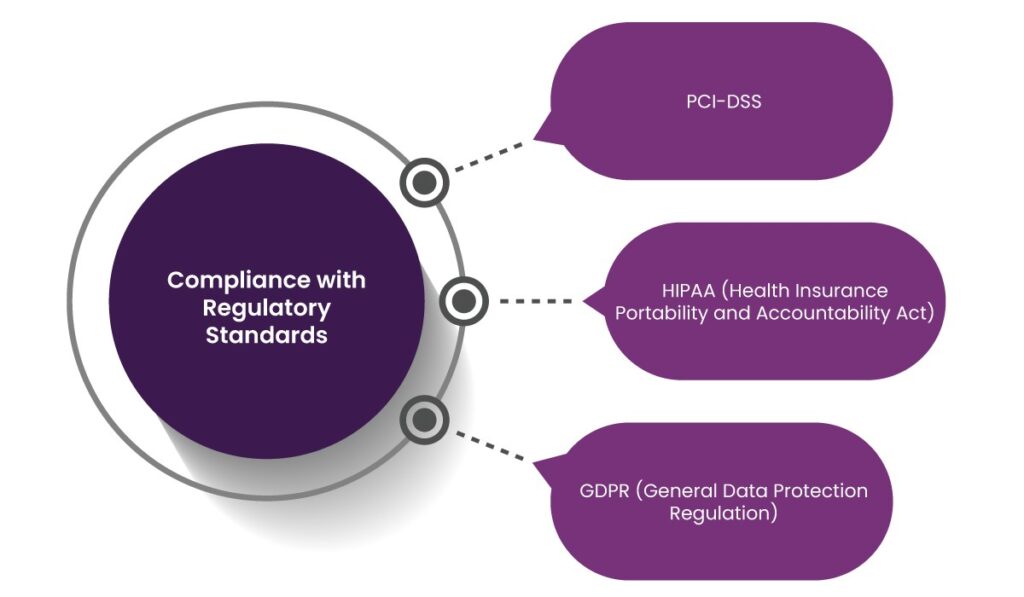
Paynova’s solutions are designed to align with these compliance standards, ensuring seamless and secure payment processing for healthcare organizations.
5. AI-Powered Fraud Detection and Prevention
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a crucial role in detecting and preventing payment fraud. AI-powered systems analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies in real time.
- Identifies suspicious transactions based on behavioral analysis.
- Prevents fraudulent activities before they impact healthcare providers.
- Continuously learns and adapts to new fraud techniques.
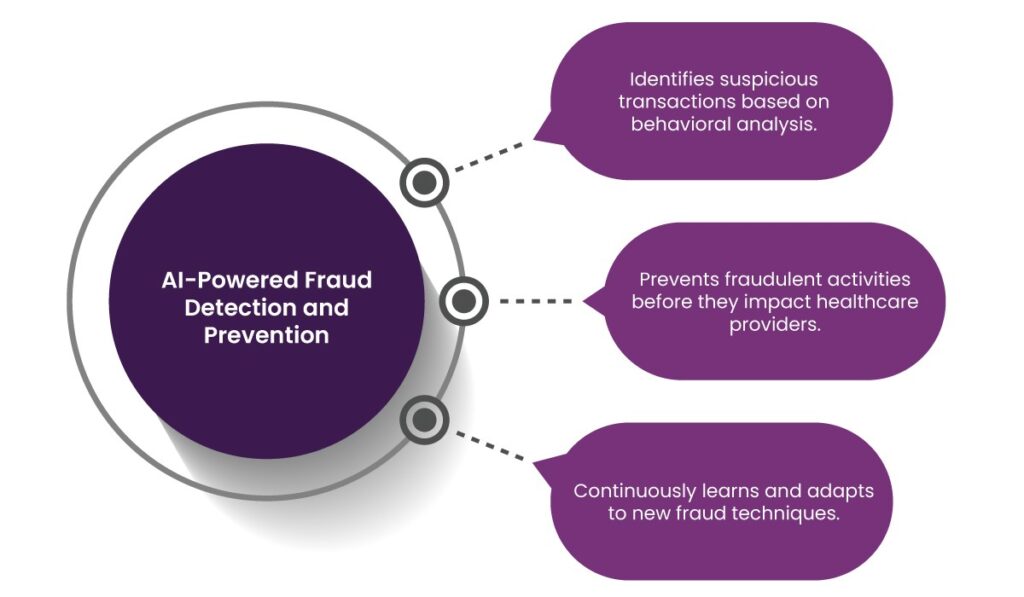
Paynova employs AI-driven fraud detection algorithms to ensure safe and secure healthcare transactions.
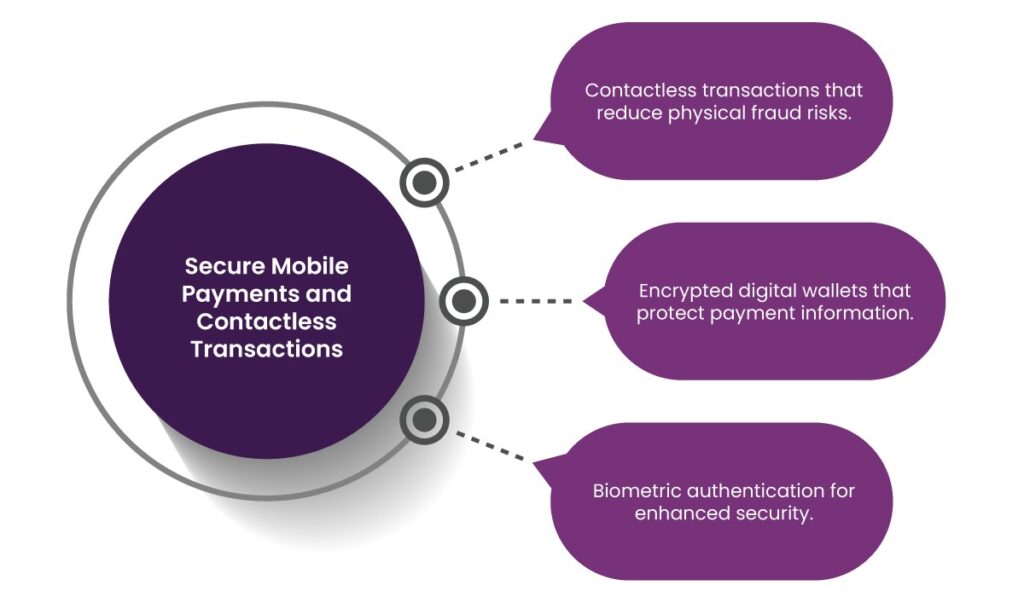
6. Secure Mobile Payments and Contactless Transactions
As mobile and contactless payments become increasingly popular in healthcare, ensuring their security is paramount. Secure mobile payment solutions offer:
- Contactless transactions that reduce physical fraud risks.
- Encrypted digital wallets that protect payment information.
- Biometric authentication for enhanced security.

Paynova provides encrypted mobile payment solutions that facilitate seamless and secure transactions in healthcare facilities.
7. Secure Mobile Payment Systems
With the rise of telemedicine and mobile healthcare services, secure mobile payment options are essential. Healthcare providers should:
- Use mobile wallet solutions (Apple Pay, Google Pay) that offer encrypted transactions.
- Implement biometric authentication for in-app payments.
- Regularly update mobile apps to patch security vulnerabilities.

Ensuring that mobile payment platforms meet security standards protects both patients and providers from fraud risks.
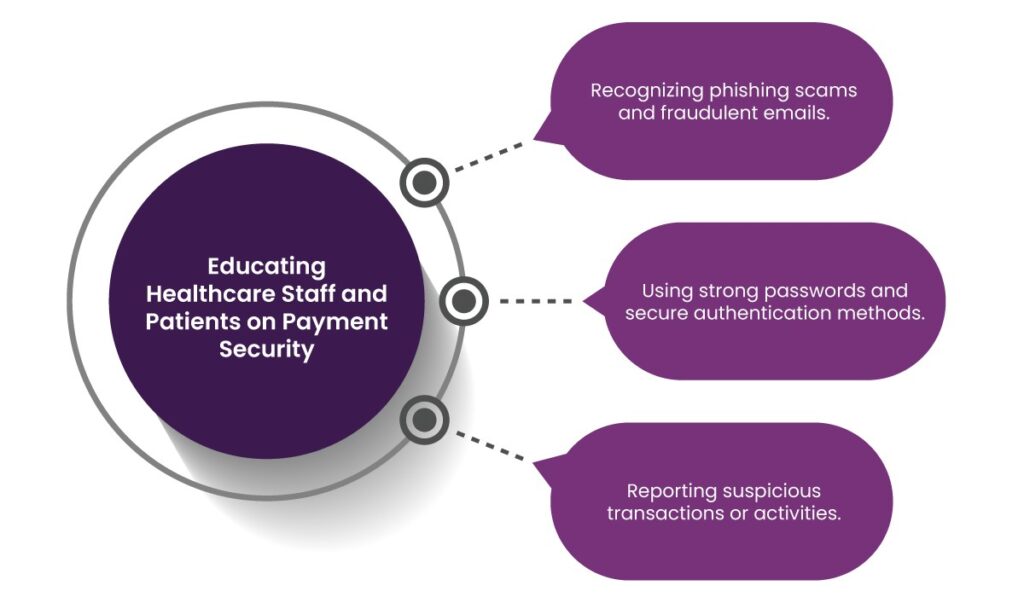
8. Educating Healthcare Staff and Patients on Payment Security
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches. Educating healthcare staff and patients about cybersecurity best practices can significantly reduce risks. Key training areas include:
- Recognizing phishing scams and fraudulent emails.
- Using strong passwords and secure authentication methods.
- Reporting suspicious transactions or activities.

By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, healthcare organizations can minimize the chances of payment fraud.
Benefits of Enhanced Payment Security in Healthcare
Implementing strong payment security measures offers several advantages for both healthcare providers and patients:
- Fraud Prevention: Reduces the risk of financial losses from fraudulent transactions.
- Data Protection: Ensures patient information remains confidential and secure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations avoid fines and legal consequences.
- Improved Patient Trust: Encourages patients to use digital payment methods with confidence.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduces manual fraud investigation efforts and enhances workflow.

Conclusion
As cyber threats grow bolder, hospitals and healthcare providers must stay one step ahead by implementing robust security measures like end-to-end encryption, tokenization, multi-factor authentication, and AI-powered fraud detection. These aren’t just buzzwords; they are the armor that protects sensitive patient information, ensures compliance with stringent regulations, and prevents financial losses.
But it’s not just about protecting data—it’s about protecting the trust patients place in healthcare institutions. When healthcare providers prioritize payment security, they don’t just secure healthcare payment systems; they foster a sense of confidence among patients that their personal and financial information is safe. This trust translates to a more secure environment for both patients and providers, where fraud and data breaches are minimized, and healthcare delivery is uninterrupted.
Paynova is an advanced, secure payment gateway built with essential features like tokenization, end-to-end encryption, and multi-factor authentication to protect your transactions. Whether you’re a healthcare provider or running an online business, our solutions ensure your data stays safe and fraud-free.
Don’t wait for a breach—secure your payments today with Paynova!
Customer also ask
- Why is payment security important in healthcare?
Payment security is crucial in healthcare because medical and financial data are prime targets for cybercriminals. Secure payment systems protect patient information, prevent fraud, and ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA and PCI-DSS.
- What are the most common types of fraud in healthcare payments?
Common types of fraud include medical identity theft, payment fraud, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in payment systems to steal sensitive data or demand ransom.
- How does encryption help protect healthcare payments?
Encryption ensures that payment data is converted into unreadable code during transmission, preventing unauthorized access. End-to-end encryption (E2EE) safeguards patient payment details from cyber threats.
- What is tokenization, and how does it enhance security?
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with random tokens that hold no actual value. Even if hackers access the tokens, they cannot retrieve the original payment information, reducing fraud risks.
- How does multi-factor authentication (MFA) improve payment security?
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple factors, such as passwords, biometric scans, or OTPs. This prevents unauthorized access to healthcare payment systems.
- What role does AI play in fraud detection for healthcare payments?
AI-powered fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns in real time to identify and flag suspicious activities. Machine learning algorithms continuously adapt to new fraud techniques, enhancing security.
- Are mobile and contactless payments secure for healthcare transactions?
Yes, mobile and contactless payments can be secure if they use encryption, biometric authentication, and tokenization. Digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay provide an extra layer of protection.
- How can healthcare organizations ensure compliance with security regulations?
Healthcare organizations must follow standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR by implementing strong security protocols, conducting regular audits, and training staff on cybersecurity best practices.














