“The only way we can shift our health care system is if individuals begin to understand they have a basic right to their own health information.” – Elizabeth Holmes, founder of Theranos
Electronic Medical Records (EMRS) are digital versions of patients’ paper charts and have revolutionized how healthcare providers manage and store patient information. By converting traditional paper records into electronic format, EMRS make it easier for healthcare professionals to track patient history, diagnose conditions, and provide more efficient care.
But have you ever wondered how patient access to these electronic records could change how we engage with our health?
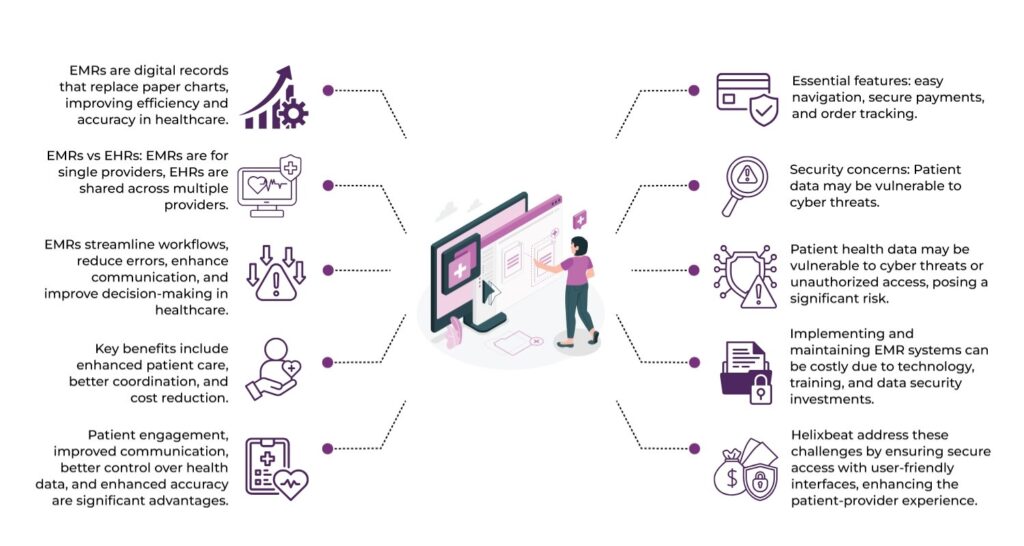
Table of Contents
Understanding Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
EMRs are digital alternatives to traditional paper charts that healthcare providers utilize to monitor a patient’s medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and other health-related data. In contrast to paper records, EMRs enable healthcare professionals to electronically store and manage patient information, enhancing both the efficiency and precision of care.
How EMRs Differ from Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Here’s a table comparing EMRs and EHRs with key differences
| Aspect | Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) | Electronic Health Records (EHRs) |
| Definition | Digital version of patient records within a single healthcare provider. | A more comprehensive, shared digital record across multiple healthcare providers. |
| Scope | Limited to one healthcare provider or practice. | Shared across multiple healthcare settings, including specialists, hospitals, and labs. |
| Data Focus | Contains data specific to one provider, such as diagnoses, treatments, and medications. | Includes a full view of a patient’s medical history from various providers. |
| Integration | Often not designed to communicate with other providers’ systems. | Designed to enable data sharing and interoperability across systems. |
| Access | Accessible only by the provider or practice managing the records. | Accessible by authorized users across different providers and systems. |
Role of EMRs in Modern Healthcare Systems
(Note:Please create an infographic like the image given below and add the subheadings written below)
Streamlining Workflows
- Digital records replace paper, reducing administrative burdens.
- Faster access to patient information, improving operational efficiency.
Improving Accuracy and Reducing Errors
- Minimizes human errors like illegible handwriting or lost records.
- Up-to-date, accurate information accessible at the point of care.
Enhancing Communication
- Facilitates better coordination between healthcare providers.
- Easy sharing of patient information among specialists, reducing redundancy.
Better Decision-Making
- Immediate access to patient history aids in quicker diagnoses and treatment.
- Decision support tools integrated into EMRs help providers make informed choices.
Improving Patient Care
- Allows healthcare providers to track long-term health progress.
- Reduces gaps in care, ensuring a comprehensive view of the patient’s health.
Facilitating Patient Engagement
- Empowers patients with access to their own health data, increasing involvement.
- Enables patients to make informed decisions and actively manage their health.
Regulatory Compliance
- Helps healthcare providers comply with HIPAA and other regulations.
- EMRs help in securely storing and managing patient data, maintaining privacy standards.
Data Security and Privacy
- Enhanced security features protect sensitive patient information.
- Encryption and access control ensure that only authorized personnel can view records.
Cost Efficiency
- Reduces costs associated with paper records, filing systems, and physical storage.
- Lowers the risk of costly medical errors or redundant tests due to missing information.
Benefits of Electronic Health Records
- Enhanced Quality of Patient Care
- Improved Coordination of Care
- Greater Operational Efficiency
- Decreased Medical Mistakes
- Boosted Patient Safety
- Quicker Access to Patient Information
- Facilitation of Preventive Care
- Better Patient Involvement
- Adherence to Regulations
- Informed Decision Making Based on Data
Pros and Cons of Patient Access to Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
(Note: Please create an infographic based on the table)
| Pros of Patient Access to EMRs | Cons of Patient Access to EMRs |
| Increased Patient Engagement | Privacy and Security Risks |
| Improved Communication with Healthcare Providers | Misinterpretation of Medical Data |
| Better Control Over Health Information | Increased Patient Anxiety |
| Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors | Technical Barriers |
| Convenient Access to Medical History | Cost of Implementation and Maintenance |
Pros of Patient Access to EMRs
Electronic medical records are recognized for improving healthcare efficiency, enhancing care quality, and reducing costs compared to paper records.
Increased Patient Engagement
- Patient access to Electronic Medical Records fosters a more involved healthcare experience.
- Patients can actively track lab results, prescriptions, and upcoming appointments.
- This increased involvement enhances their commitment to health management.
Improved Communication with Healthcare Providers
- Access to EMRs allows for easier and faster communication with healthcare providers.
- Patients can message doctors directly, ask questions, or clarify treatment instructions.
- This results in a more collaborative and efficient healthcare relationship.
Better Control Over Health Information
- Patients have the ability to manage and review their personal health data.
- They can update contact details, preferences, or medical history, ensuring accuracy.
- This level of control contributes to more tailored and precise care.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduces Errors
- EMRs reduce the chances of mistakes due to misplaced files or illegible handwriting.
- Real-time updates and shared access to patient information improve data accuracy.
- This helps ensure that healthcare providers have the most up-to-date details when making decisions.
Convenient Access to Medical History
- Patients can access their entire medical history securely and at any time.
- This access is particularly useful during emergency situations or when visiting a new provider.
- It also allows patients to track their treatment progress and review past diagnoses.
Cons of Patient Access to EMRs
Privacy and Security Risks
- Patient health information can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks and unauthorized access.
- Sharing EMR data online or across platforms increases the risk of exposure to sensitive information.
- Some healthcare systems may not have advanced security measures, leaving data at risk.
Misinterpretation of Medical Data
- Patients may struggle to understand complex medical terminology or clinical information.
- Without professional guidance, patients may misinterpret their records, leading to unnecessary worry or incorrect conclusions.
- Medical updates may confuse patients, especially when they don’t understand the context or significance.
Increased Patient Anxiety
- Patients can feel anxious when presented with detailed medical records or new conditions they weren’t aware of.
- Seeing unfamiliar medical terms or potential issues in their records can cause unnecessary stress.
- Inadequate explanations from healthcare providers may lead patients to feel more anxious about their health.
Technical Barriers
- Some patients may not have access to digital tools or reliable internet connections to access their EMRs.
- Older adults or those with limited tech experience may struggle to navigate EMR systems.
- Variations in software or devices might cause issues when accessing or updating records.
Cost of Implementation and Maintenance
- Implementing patient access to EMRs requires significant financial investment in technology and infrastructure.
- Continuous maintenance, system updates, and patient data security efforts add to long-term costs.
- Training staff and patients to use the system properly can lead to additional time and financial investments.
The Bottom Line
Access to Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) provides benefits like improved coordination and quicker access to health data, but it also poses challenges such as privacy concerns and the risk of misinterpreting medical information. These issues can create anxiety for patients and affect their ability to utilize EMRs effectively.
Solutions like PULSE by Helixbeat address these challenges by offering secure, real-time access to patient records with advanced encryption and user-friendly interfaces. This empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions without compromising security. By adopting PULSE, healthcare systems can reduce risks associated with EMRs, enhancing the overall experience for everyone involved.
Take the next step toward secure and efficient patient data management. Contact us today to learn how PULSE by Helixbeat can help!
FAQs
What are the pros and cons of electronic medical records?
Pros: Better access to patient data, improved accuracy, faster sharing.
Cons: High setup costs, data security concerns, potential technical issues.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of electronic records?
Advantages: Real-time updates, reduced paperwork, better coordination of care.
Disadvantages: System downtimes, learning curve for staff, risk of breaches.
What are the benefits of electronic patient records?
Electronic patient records help streamline treatment decisions, boost patient safety, and support faster provider communication.
What is a disadvantage of charting in an electronic health record system?
A common drawback is screen time charting may reduce face-to-face interaction with patients and lead to documentation fatigue.
Are EMRs more secure than paper records?
Yes, EMRs are generally more secure than paper records due to encrypted data storage, access controls, and easier tracking of user interactions, which reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Can patients access their own EMRs?
Yes, many healthcare systems allow patients to access their electronic medical records systems, empowering them to view their health information and communicate with providers.














