Healthcare data interoperability has long been and continues to be a major problem for healthcare facilities. The main challenges that prevented different medical organizations from sharing health information were fragmented systems and disparate, incompatible standards. In the evolving healthcare era, FHIR plays a remarkable role in interoperability.
Unlike outdated methods, FHIR resurfaces smooth healthcare interoperability. The need for healthcare developers and physicians to comprehend FHIR resources, components, and operation is growing, along with the demand for HL7 FHIR implementation services.
In this post, we will dissect the primary components of the FHIR standard to clarify the fundamentals of this framework and provide useful examples. By the end, you will understand FHIR’s significance for your company and the how and why of its expanding role in enhancing healthcare interoperability.
Table of Contents
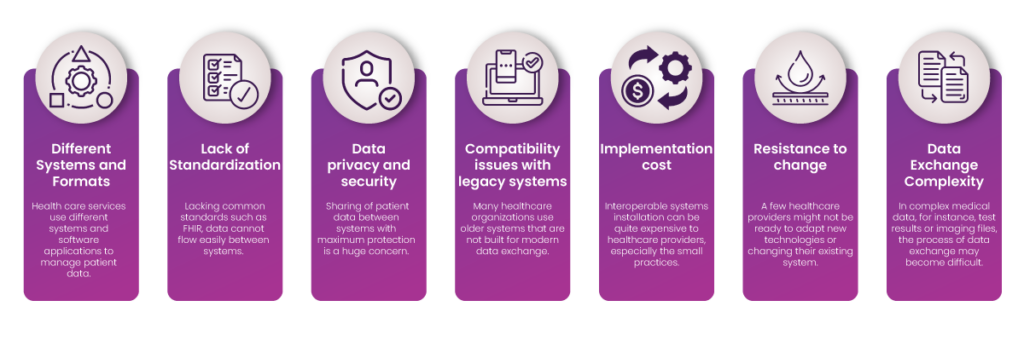
Understanding the Challenges of Healthcare Interoperability:
- Different Systems and Formats: Healthcare services use different systems and software applications to manage patient data. Each system stores information in different formats, making sharing data in other systems difficult.
- Lack of Standardization: Without common standards such as FHIR, data cannot flow easily between systems. This leads to healthcare interoperability issues such as confusion, delays, and errors in patient care services.
- Data privacy and security: Sharing patient data between systems with maximum protection is a considerable concern. Strict privacy laws, like HIPAA, require that sensitive information be handled very carefully to avoid breaches.
- Compatibility issues with legacy systems: Many healthcare organizations use older systems that are not built for modern data exchange. Upgrading or replacing such systems is expensive and time-consuming.
- Implementation cost: Installing interoperable systems can be quite expensive for healthcare providers, especially small practices. Upgrading technology and training personnel is also expensive, slowing progress.
- Resistance to change: Some healthcare providers might not be ready to adapt to new technologies or change their existing systems, which can slow the implementation of healthcare interoperability solutions.
- Data Exchange Complexity: The process of data exchange may become difficult for complex medical data, such as test results or imaging files. The issue is making the data accurate, complete, and understandable.
For example:
Sarah, a patient with diabetes, faces constant frustration without FHIR technology. When she visits her primary doctor, she must explain her medical history again to each specialist she sees, like her endocrinologist. Her prescriptions often get delayed because the pharmacy doesn’t automatically receive her updates. Additionally, her insurer struggles to process claims accurately due to inconsistent data formats between providers. Sarah spends hours filling out forms, repeating her information, and waiting for test results. Without a unified system like FHIR, her healthcare journey becomes disjointed, slow, and prone to errors, leading to unnecessary stress and confusion.
The Role of FHIR in Modern Healthcare
What is FHIR?
The FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standard defines how healthcare information can be exchanged between different computer systems, regardless of how it is stored in those systems. It will enable clinical and administrative data and any other healthcare information to be securely accessible to only those who need to access them and those who are entitled to do so for the good of a patient receiving care.
Unlike the older standards HL7 v2 and Clinical Document Architecture (CDA), FHIR utilizes the latest Web technologies: RESTful APIs, JSON, and XML to facilitate integration and implementation.
It is primarily designed on the principle of “resources.” The FHIR resources are modular and reusable building blocks for the important entities of the healthcare domain, including:
- Patients
- Medications
- Observations
- Care Plans
Such standardized resources ensure that data exchange occurs smoothly across various systems and in multiple formats without worrying about the underlying systems.
The Role of FHIR in Modern Healthcare
FHIR is a technical standard and an entirely new modern healthcare system. Once the healthcare institution simplifies data exchange and standardizes it appropriately, it will ease the complexity of fragmented systems. It helps hospitals and healthcare stakeholders gain actionable insights and real-time information. Here are three pivotal contributions of FHIR:
1. Healthcare Interoperability
FHIR is at the forefront of breaking down barriers between healthcare systems. It enables seamless data flow across diverse platforms like EHRs, mobile health apps, and IoT devices. This ensures that critical medical information is accessible where and when it is needed, fostering better care coordination, smooth healthcare interoperability and minimizing redundant tests.
2. Patient-Centered Care
FHIR puts patients at the centre of the health ecosystem. It empowers them with direct access to their medical records through personal health applications, hence building transparency and trust. It puts control over their data-sharing preferences and makes them active participants in their own health journey.
3. Innovation
FHIR is an advanced technology that could support artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and telemedicine applications. For instance, integration with wearable devices can be fed into patient care plans that monitor patients in real-time. Moreover, FHIR’s modularity has the potential to streamline innovation in healthcare application development, such as decision support tools and personalized care plans.
By addressing healthcare interoperability challenges, enhancing patient engagement, and enabling technological advancements, FHIR transforms healthcare delivery. Its adoption drives better outcomes, operational efficiency, and innovation, setting the stage for a connected, patient-centred healthcare ecosystem.

Key Features of FHIR Unified Solutions: A Comprehensive Overview
The healthcare industry faces constant challenges in managing and exchanging data across disparate systems. Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) addresses these issues by offering a unified solution that enhances healthcare interoperability, efficiency, and patient care. Below, we explore the key features of FHIR Unified Solutions and their transformative potential in healthcare.
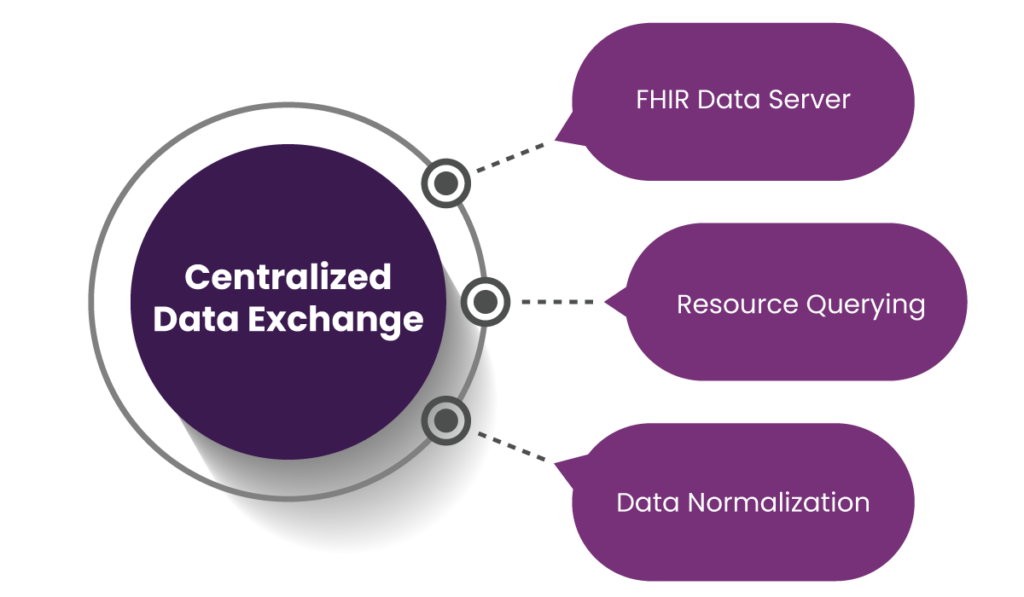
1. Centralized Data Exchange
Centralized data exchange is the foundation of FHIR, enabling the seamless integration of diverse healthcare systems into a cohesive ecosystem.
FHIR Data Server
A core component of FHIR is the FHIR Data Server, which serves as a centralized repository. It stores and exchanges FHIR resources such as patient records, medication details, and diagnostic reports. By consolidating data into one system, healthcare organizations reduce redundancy, improve accessibility, and streamline workflows.
Resource Querying
FHIR utilizes RESTful APIs, a modern approach to web communication, for querying and modifying resources. This facilitates efficient data access and allows developers to quickly retrieve, update, or delete records. For example, a healthcare provider can instantly pull a patient’s latest lab results during a consultation.
Data Normalization
Healthcare Interoperability often suffers due to data inconsistency between systems. FHIR addresses this with data normalization, converting information from various legacy systems into standardized, FHIR-compatible formats. This ensures data reliability and paves the way for consistent and accurate healthcare delivery.
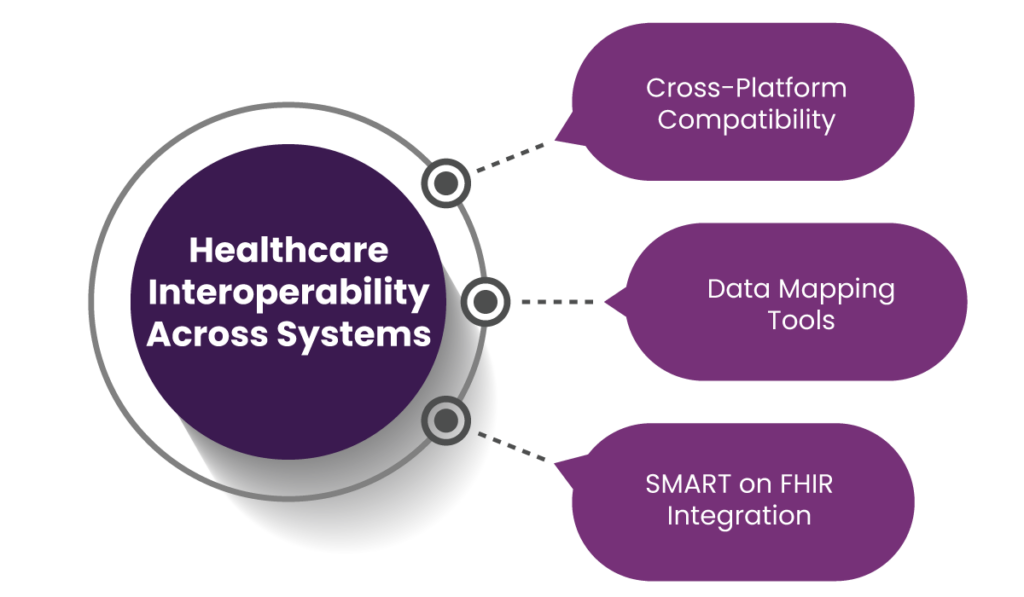
2. Healthcare Interoperability Across Systems
FHIR’s design prioritizes healthcare interoperability, enabling different systems to communicate effectively.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
FHIR supports seamless integration across diverse platforms, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), laboratory information systems, mobile applications, and IoT devices. This compatibility ensures that healthcare providers and patients have access to data, regardless of the source system.
Data Mapping Tools
One of the standout features is FHIR’s ability to integrate with older data formats like HL7 v2 and Clinical Document Architecture (CDA). Organizations can convert legacy data into FHIR resources using data mapping tools, maintaining backward compatibility while adopting modern standards.
SMART on FHIR Integration
FHIR supports the Substitutable Medical Applications, Reusable Technology (SMART) framework, which allows third-party applications to access data securely. This enhances system functionality, enabling the integration of advanced tools such as mobile health apps, clinical decision support systems, and patient portals.
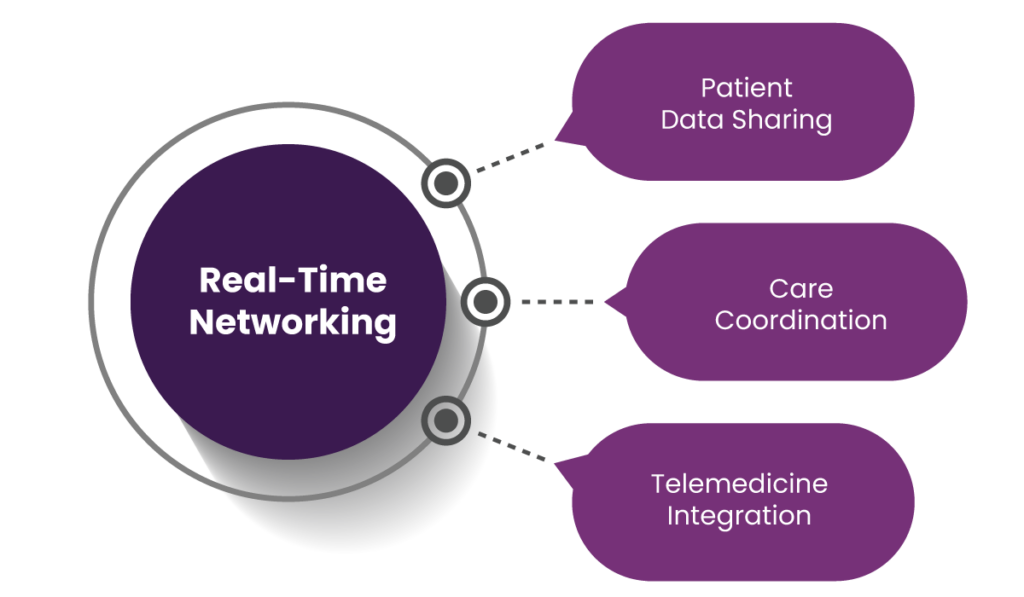
3. Real-Time Networking
In an era of rapid healthcare delivery, real-time data exchange is critical. FHIR facilitates instant data sharing, ensuring providers and patients can make timely decisions.
Patient Data Sharing
FHIR enables the instantaneous sharing of critical patient information, such as medical histories, lab results, and prescriptions. For example, a specialist can review a primary care physician’s notes in real time, leading to better-informed diagnoses and treatment plans.
Care Coordination
Collaboration is at the heart of adequate healthcare. FHIR promotes care coordination by connecting primary care providers, specialists, and allied health professionals. This ensures a unified approach to patient care, reducing the risk of errors and redundant treatments.
Telemedicine Integration
The rise of telemedicine has made real-time networking even more vital. FHIR supports virtual consultations by providing instant access to patient data, enabling remote providers to offer high-quality care without geographical limitations and ensuring smooth healthcare interoperability.
4. Advanced Data Security
With sensitive patient information at stake, FHIR incorporates robust security measures to safeguard data.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
FHIR employs RBAC, which restricts data access based on user roles. For instance, a nurse may access a patient’s vital signs but not their insurance details, ensuring privacy and compliance.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption, which protects information during transmission and storage, further enhances data security. Protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) ensure that patient data remains confidential.
Consent Management
FHIR empowers patients to control their data through consent management tools. These allow individuals to define sharing permissions, aligning with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
5. Patient-Centered Functionality
FHIR puts patients at the forefront by enabling them to take an active role in their healthcare journey.
Personal Health Records (PHR)
Patients can securely access their medical records via PHR systems built on FHIR. This transparency fosters trust and allows individuals to understand better and manage their health.
Remote Monitoring Integration
FHIR supports data collection from wearables and IoT devices like fitness trackers and glucose monitors. This enables continuous care, allowing providers to monitor patients remotely and intervene when necessary.
Interoperable Care Plans
Healthcare interoperability plans are shared and updated in real time to facilitate collaboration between patients and healthcare teams. This ensures everyone involved in a patient’s care is on the same page.
6. Analytics and Decision Support
FHIR’s robust analytics capabilities help organizations harness data for informed decision-making.
Population Health Management
FHIR aggregates anonymized data, enabling healthcare providers to identify trends, predict outbreaks, and optimize care delivery for large populations.
AI-Driven Insights
FHIR transforms raw data into actionable insights by integrating with artificial intelligence tools. For instance, predictive analytics can identify patients at risk of chronic conditions, allowing for early intervention.
Operational Analytics
Healthcare organizations can use FHIR to track system usage, monitor resource allocation, and identify areas for improvement. This operational insight drives efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
7. Scalability and Adaptability
FHIR’s modular and flexible architecture ensures it can adapt to evolving healthcare needs.
Cloud-Based Architecture
FHIR supports cloud-based deployment, which allows organizations to scale their infrastructure based on demand. This is particularly useful for handling sudden surges in data, such as during public health emergencies.
FHIR Profiles
Customization is a key feature of FHIR. Organizations can create FHIR Profiles to tailor the standard to specific needs, such as regional regulations or specialized workflows.
Modular Design
FHIR’s modular approach enables the addition of new functionalities without disrupting existing systems. For example, a hospital can integrate a telemedicine feature into its FHIR solution without overhauling its entire IT infrastructure.
8. Workflow Automation
Automation is essential for reducing manual effort and improving operational efficiency.
Automated Data Exchange
FHIR synchronizes records across systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry. This not only saves time but also minimizes errors.
Referral Automation
By automating referrals, FHIR ensures that patients are directed to the right specialists with real-time updates. This speeds up the care delivery process and enhances patient satisfaction.
Alerts and Notifications
FHIR enables automated alerts for appointments, medication refills, and test results. These notifications help patients stay on track with their healthcare plans, improving adherence and outcomes.
How FHIR Transforms Healthcare Interoperability
Sarah, a patient in the USA, often visits multiple healthcare providers for her needs. Every year, she goes for an annual check-up with her primary doctor. She also manages her diabetes with an endocrinologist and frequently refills her prescriptions at the pharmacy. When it’s time to process her insurance claims, she has to communicate with her insurer. But here’s the challenge: Each provider uses a different system, and Sarah needs to fill out forms and explain her medical history every time she visits a new provider.
This process can be overwhelming and time-consuming. However, if a FHIR Unified Solution powered Sarah’s healthcare journey, everything would be much smoother.
With FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), Sarah’s medical information can be stored in a standardized format that all her healthcare providers can access. For example, when she visits her primary doctor for her check-up, her doctor’s office can easily share Sarah’s medical history with her endocrinologist. Sarah doesn’t have to repeat her health story or complete the same forms every visit.
The FHIR system allows Sarah’s medical data to be shared in real-time across different providers. If she needs a specialist consultation, the endocrinologist can instantly access her primary doctor’s records, allowing them to coordinate care more efficiently. Sarah is also in control of her medical data. Through a secure app, she can manage who has access to her information and when.
Furthermore, the FHIR solution streamlines the entire process. When Sarah needs a prescription refill, the system automatically sends the details to her pharmacy and insurance company. This eliminates the need for Sarah to share her prescription information manually, saving her time and reducing errors.
In short, FHIR offers Sarah a seamless, automated, and empowered healthcare experience, where her data flows smoothly between providers, making her healthcare journey more efficient and less stressful.
Example Use Cases of FHIR
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) has many practical use cases that help improve healthcare delivery. Here are some examples:
- Hospital Networks: FHIR enables hospitals and healthcare facilities to share patient data seamlessly. This reduces redundant tests and ensures better coordination of care. For instance, if a patient moves from one hospital to another, their medical records can be accessed instantly, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment.
- Integrated Telehealth: With FHIR, telehealth platforms can access real-time patient data during remote consultations. Doctors can view up-to-date medical histories, test results, and treatment plans, allowing them to provide informed care, even when not physically present.
- Clinical Research: FHIR facilitates aggregating standardized data from multiple healthcare centres for clinical trials. Researchers can access a wide variety of patient data while ensuring consistency and accuracy, leading to better research outcomes and faster advancements in medical knowledge.
- Insurance Claims: FHIR streamlines the insurance claims process by automating the submission and processing of claims. Insurers can quickly verify claims with standardized data exchange, reducing administrative delays and errors.
- Public Health Surveillance: FHIR enables the use of de-identified patient data for public health monitoring. This allows health authorities to track disease outbreaks and identify health trends, improving responses to public health threats.
Benefits of a FHIR Unified Solution
A FHIR Unified Solution offers several benefits that can significantly improve healthcare delivery and streamline operations for providers, patients, and insurers. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced healthcare Interoperability: One of the biggest challenges in healthcare is the fragmentation of patient data across different systems. FHIR solves this by providing a standardized format for data exchange. This eliminates data silos, ensuring that healthcare providers can easily communicate with each other, regardless of the systems they use. For example, if a patient visits different specialists, each one can access the same medical records, ensuring continuity of care and reducing the risk of errors or duplication of tests.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Real-time data sharing between healthcare providers empowers clinicians to make informed, timely decisions. For instance, if a patient’s test results or medical history are instantly available, the healthcare provider can quickly diagnose and treat the patient. This immediate access to accurate information improves the quality of care, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Operational Efficiency: FHIR streamlines workflows by automating many tasks, such as sending prescriptions to pharmacies or processing insurance claims. This reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers and insurers, allowing them to focus more on patient care. Additionally, it minimizes the risk of human error, as manual data entry is reduced.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing: FHIR is designed to be flexible and adaptable. FHIR can support new technologies, data formats, and regulations as healthcare evolves, ensuring that systems remain up-to-date and scalable. This future-proofing is crucial for healthcare organizations looking to innovate and expand over time.
Considerations for Implementing FHIR
When implementing FHIR, several key considerations are crucial for success:
- Governance: Establish clear policies for data sharing, security, and compliance to ensure that all processes align with legal and regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA in the USA. This ensures data privacy and integrity.
- Training: Equip staff with a thorough understanding of FHIR standards and workflows. Proper training ensures efficient use of the system, reduces errors, and maximizes adoption among healthcare providers.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with technology vendors and stakeholders to ensure compatibility and smooth integration of FHIR with existing systems. This will promote seamless data exchange across healthcare providers.
Why Fusion’s FHIR?
Fusion’s FHIR is a robust solution designed to streamline healthcare interoperability by leveraging the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard. It enables seamless, real-time data exchange across various healthcare systems, ensuring that patient information is accessible and up-to-date. Fusion’s FHIR is particularly valuable for healthcare organizations seeking to integrate disparate data sources, providing enhanced efficiency, improved patient care, and better decision-making.
By supporting secure, scalable, and customizable APIs, Fusion’s FHIR accelerates the adoption of modern healthcare technologies while ensuring compliance with industry regulations like HIPAA, making it an essential tool for today’s digital health ecosystem.
A Day in the Life of Fusion’s FHIR: Simplifying Healthcare Data Exchange
Let’s revisit Sarah’s journey, now empowered by FHIR:
- Morning: Sarah visits her primary doctor, who updates her medical records.
- Afternoon: Her endocrinologist retrieves her updated records for a consultation.
- Evening: Sarah’s new prescription is sent directly to her pharmacy and insurer.
Thanks to FHIR, Sarah experiences a seamless and efficient healthcare journey, free from redundant paperwork and delays.
Conclusion
FHIR is more than just a technical standard; it is a transformative force in healthcare interoperability. By unifying diverse data sources, enabling real-time communication, and empowering patients, FHIR paves the way for a collaborative and efficient healthcare ecosystem. As healthcare systems continue to evolve, the adoption of FHIR will be instrumental in delivering patient-centred care, improving outcomes, and driving operational excellence.
In a world where timely and accurate healthcare data can make the difference between life and death, FHIR stands as the backbone of healthcare interoperability, ensuring that no patient falls through the cracks of fragmented systems.
For a FUSION, embracing FHIR means embracing more than the next generation of technology—it means embracing a whole new paradigm toward a healthier, more patient-centric healthcare ecosystem. Let’s tap into FHIR’s full potential to unlock possibilities for a healthier future.
Frequently asked question
1. What is FHIR, and why is it important in healthcare?
- Answer: FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a standard for exchanging healthcare data electronically. It allows different healthcare systems to share and access data seamlessly, improving patient care, reducing errors, and streamlining healthcare processes.
2. How does FHIR improve healthcare interoperability?
- Answer: FHIR enables healthcare systems, like electronic health records (EHR) and health information exchanges, to communicate with each other more effectively. It uses modern web technologies like RESTful APIs, making it easier to access and share patient data securely across platforms.
3. What are the main components of FHIR?
- Answer: FHIR is composed of several key components, including resources (standardized data formats), profiles (specific use cases for resources), and extensions (customized data fields). These elements work together to ensure flexibility and interoperability in healthcare data exchange.
4. What is the role of SMART on FHIR in healthcare applications?
- Answer: SMART on FHIR is a platform that allows third-party apps to integrate with EHR systems. It provides a secure way for healthcare developers to build applications that can access patient data, ensuring that the data exchange is safe, compliant, and efficient.
5. How does FHIR enhance patient care?
- Answer: FHIR improves patient care by ensuring that accurate, up-to-date medical information is accessible across different healthcare providers and systems. This reduces the chances of medical errors, ensures better coordination among care teams, and allows patients greater control over their health data.
6. Can FHIR be used with existing healthcare systems?
- Answer: FHIR is designed to be compatible with existing healthcare systems. It can be implemented in legacy systems using APIs and integration tools, allowing healthcare providers to adopt FHIR without replacing their entire infrastructure.
7. What challenges does FHIR face in healthcare adoption?
- Answer: Some challenges include the initial costs of implementation, integration with existing systems, data security concerns, and ensuring all healthcare stakeholders adopt and follow FHIR standards. However, these challenges are being addressed as FHIR adoption grows.
8. Is FHIR secure for handling sensitive patient data?
- Answer: FHIR ensures that patient data is exchanged securely through encryption and authentication protocols. It complies with privacy regulations like HIPAA to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient information.
9. How can developers use FHIR to create healthcare applications?
- Answer: Developers can use FHIR APIs to build applications that securely access patient data. By using SMART on FHIR, developers can create apps that integrate with EHRs, allowing healthcare professionals to access the correct data at the right time and improving decision-making and patient outcomes.
10. What are some real-world examples of FHIR in use today?
- Answer: Examples include patient portals that allow individuals to access their medical records, mobile health apps that sync with healthcare providers’ EHRs, and systems that help doctors and nurses track patient data in real time. These applications use FHIR to enhance communication and improve the quality of care.













