Healthcare organizations are all about patient outcomes, but there are lots of other operational priorities that need to be managed to support that goal. One of those is ensuring secure payments processes.
When it comes to payments, healthcare organizations are like every other entity that accepts card payments. They have to follow HIPAA set by US government. These standards continue to evolve to address new security concerns, and IT teams need to keep up to protect patients as well their own organizations.
With the rise of electronic health records (EHRs), telehealth services, and digital payment systems, healthcare providers face increasing challenges in protecting sensitive patient data. Compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the implementation of advanced security measures have become paramount.
This blog will educate you on the significance of secure payments systems for healthcare providers, highlights the challenges in achieving them, and examines how PayNova addresses these critical needs.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Secure Payments in Healthcare
The ransomware attack on UnitedHealth Group’s subsidiary, Change Healthcare, in 2024 was among the most significant cyberattacks in U.S. healthcare history. This incident disrupted critical functions, including claims processing and prescription drug processing, highlighting vulnerabilities in healthcare payment systems
The healthcare industry is constantly changing as billing becomes more complex and digitalized. Since hospital payment methods are becoming more digital, all US healthcare providers must ensure their payment gateway complies with legal requirements. One important component that determines the patient-provider interaction is secure payments mechanisms. The healthcare provider is responsible for making sure patient data is shielded from unwanted access. In addition to fostering trust, that enhanced the hotels’ reputation. Healthcare providers may face harsh financial penalties if they do not comply.
The Role of HIPAA in Payment Security
HIPAA sets the standard for safeguarding protected health information (PHI). The act mandates covered entities—healthcare providers, insurers, and their business associates—to implement robust physical, technical, and administrative safeguards. It protect sensitive data like insurance details, billing information, and medical history, is not exposed to unauthorized individuals or systems during payment transactions.
- Failure to comply with HIPAA’s security standards can lead to severe penalties, including fines and legal consequences.
- HIPAA requires that healthcare providers maintain comprehensive audit trails of all transactions, including payment processes.
- Healthcare providers must ensure that any third-party vendor or business associate involved in payment processing, such as payment gateways or billing systems, is HIPAA-compliant.
- To prevent unauthorized access to sensitive payment and healthcare data, HIPAA requires strong authentication procedures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and detailed access controls.
- HIPAA requires healthcare providers and insurers to implement encryption protocols(Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS)) and other security measures to protect PHI during electronic transactions.
Challenges in Ensuring Secure Payments
Despite the advancements in technology and regulatory frameworks, healthcare providers face several challenges in ensuring secure payments systems:
Complex Regulatory Landscape:
Navigating the intricacies of HIPAA compliance and staying updated with amendments and supplementary acts like HITECH requires continuous monitoring and expertise. Healthcare providers must ensure that their payment systems and data management practices align with these regulations, which often demand significant investments in legal counsel, compliance audits, and technology upgrades. Additionally, the evolving nature of these regulations creates uncertainty, making it challenging to implement long-term strategies without the risk of non-compliance.

Cybersecurity Threats:
The healthcare sector is a prime target for cyberattacks due to the high value of Protected Health Information (PHI) on the black market. Ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and data breaches are common threats that can compromise sensitive information. Healthcare organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security assessments to mitigate these risks. The growing sophistication of cybercriminals also means that organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their defense strategies.

Integration with Legacy Systems:
Many healthcare organizations still rely on outdated systems that are not equipped to handle modern security protocols. These legacy systems often lack the ability to integrate seamlessly with advanced encryption technologies and secure payments gateways, leaving vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. Upgrading or replacing these systems is a complex and costly process that requires careful planning to avoid disruptions to critical healthcare services.

Telehealth Expansion:
The surge in telehealth services has increased the volume of electronic transactions, amplifying the need for secure data transmission over public and private networks. Telehealth platforms must ensure end-to-end encryption to protect patient data during virtual consultations and payment processes. However, the rapid adoption of telehealth services often outpaces the implementation of necessary security measures, creating potential vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.

Third-Party Vendors:
Dependence on external vendors for billing, payment processing, and data management introduces additional points of vulnerability. Ensuring that all vendors comply with HIPAA standards is a persistent challenge, as it requires rigorous vetting processes, contractual agreements, and continuous monitoring. Vendors who fail to uphold these standards can expose healthcare organizations to compliance risks and security breaches, highlighting the importance of thorough due diligence.

Insider Threats:
Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data may unintentionally or maliciously compromise security. Insider threats can arise from careless handling of data, unauthorized access, or deliberate actions to exploit vulnerabilities. To address this challenge, healthcare organizations must implement robust training programs, access controls, and monitoring systems to detect and mitigate potential threats from within their workforce.

Device Proliferation:
The use of mobile devices, IoT-enabled medical equipment, and patient portals increases the attack surface, necessitating comprehensive endpoint security measures. These devices often lack standardized security protocols, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Implementing policies for secure device usage, regular updates, and multi-factor authentication can help mitigate the risks associated with device proliferation.

Data Interoperability:
The need for seamless data exchange among providers, payers, and patients can conflict with security protocols, creating a tension between usability and protection. Interoperability efforts must balance the demand for accessible and efficient data sharing with the necessity of maintaining robust security measures. Developing standardized protocols and leveraging secure data-sharing technologies can help address this challenge.

High Implementation Costs:
Deploying advanced encryption, secure payments gateways, and compliance monitoring tools can be financially burdensome, particularly for smaller practices. These costs include purchasing new technologies, hiring skilled personnel, and conducting regular security audits. Small and medium-sized healthcare providers may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to these initiatives, increasing their vulnerability to security breaches.

Human Error:
Simple mistakes, such as weak passwords or misconfigurations, can lead to significant breaches. Continuous training and awareness programs are crucial to mitigating this risk. Healthcare organizations must prioritize educating their staff on best practices for cybersecurity, including recognizing phishing attempts, securing devices, and adhering to data protection policies. Regular drills and updates can reinforce these practices and reduce the likelihood of human error.

Case Study: The Cost of Failing to Implement Secure Payments in U.S. Hospitals
In 2019, a large healthcare system in the United States faced a crippling data breach affecting over 25 million patients. Hackers exploited vulnerabilities in the hospital’s payment processing system, resulting in unauthorized access to sensitive patient information, including billing details and personal health records. The breach not only tarnished the hospital’s reputation but also led to severe financial and regulatory repercussions.
Incident Overview:
The attack stemmed from the hospital’s reliance on outdated payment processing infrastructure that lacked modern encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication. Cybercriminals infiltrated the system through a phishing email targeting an employee, gaining access to payment databases and patient health information. The breach remained undetected for over six months, during which the attackers exfiltrated sensitive data.
Consequences:
The financial impact was staggering. The hospital faced a penalty of $16 million under HIPAA regulations for failing to protect patient information adequately. Additionally, the cost of litigation, notification to affected individuals, and implementing post-breach measures exceeded $50 million. The breach also resulted in a class-action lawsuit and a loss of patient trust, leading to a decline in patient visits and revenue.
How PayNova Prevents Such Incidents:
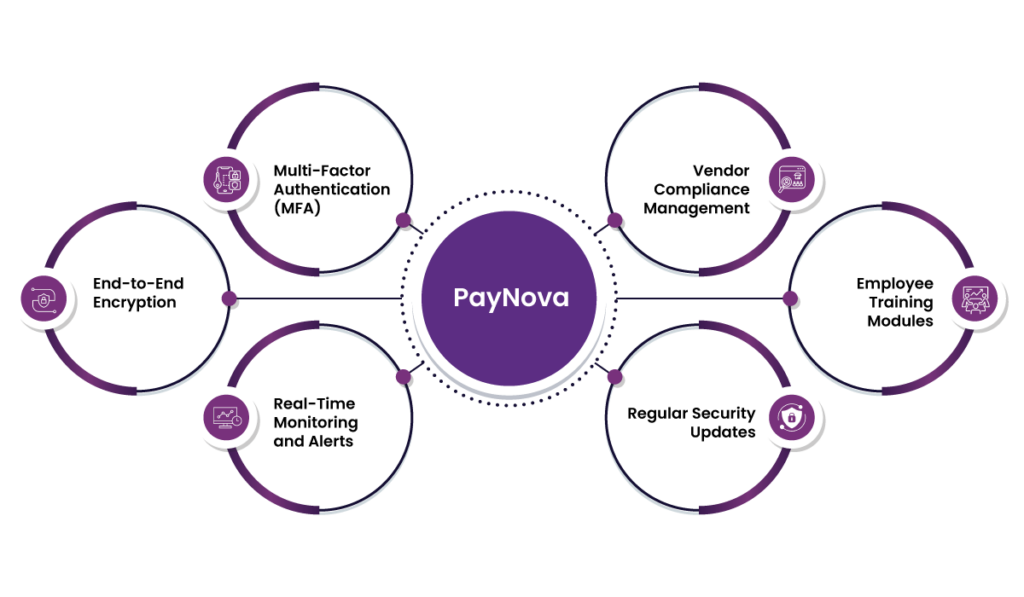
PayNova offers an advanced payment processing solution designed to comply with HIPAA and HITECH standards, mitigating the risks that led to the above breach. Here’s how:
- End-to-End Encryption: PayNova ensures all payment data is encrypted at rest and in transit, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Access to sensitive systems is safeguarded with MFA, reducing the risk of unauthorized access through compromised credentials.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: PayNova’s AI-powered systems detect anomalies in real-time, enabling immediate response to potential threats.
- Vendor Compliance Management: PayNova audits and ensures third-party vendors involved in payment processing adhere to stringent security protocols.
- Regular Security Updates: PayNova’s systems are continuously updated to address emerging cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training Modules: Recognizing that human error is a significant risk, PayNova offers training programs to educate staff on identifying phishing attempts and other cyber threats.
The Impact of PayNova’s Solutions:
Hospitals leveraging PayNova have reported zero payment-related breaches since implementation. By prioritizing data protection and compliance, PayNova not only prevents costly penalties but also fosters patient trust and operational efficiency. For the healthcare sector, adopting PayNova’s secure payments solutions is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic investment in long-term success.
Conclusion
Secure payments are not just a technical necessity—they are a cornerstone of ethical and effective healthcare delivery. As cyber threats evolve and regulatory demands increase, healthcare providers must prioritize the implementation of robust payment security systems. PayNova’s cutting-edge solutions provide the tools and expertise needed to navigate this complex landscape, ensuring compliance, protecting patient data, and fostering trust.
In a world where digital interactions define the patient experience, secure payments systems are no longer optional. They are a vital investment in the future of healthcare, enabling providers to deliver quality care while safeguarding the sensitive information that patients entrust to them.
Frequently asked question
Why is payment security important for healthcare providers?
Payment security is important to safeguard sensitive patient data, maintain compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, and avoid financial and reputational damage resulting from data breaches.
What are the key regulations that healthcare providers must follow for secure payments?
Healthcare providers are required to abide by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and other relevant laws, such as HITECH, in protecting the privacy of protected health information (PHI) when payment transactions are involved.
How does HIPAA affect payment processing systems?
HIPAA demands strong physical, technical, and administrative controls, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and audit trails, to ensure that sensitive payment and healthcare data remain secure.
What are the common challenges healthcare providers face in implementing secure payments system?
Challenges include navigating complex regulations, mitigating cybersecurity threats, integrating with legacy systems, ensuring vendor compliance, and addressing high implementation costs.
How does PayNova enhance payment security for healthcare organizations?
PayNova offers end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, real-time monitoring, vendor compliance management, and employee training programs to address vulnerabilities and ensure secure payments system.
What are the financial implications of a data breach for healthcare providers?
Data breaches can lead to heavy fines under HIPAA, litigation costs, loss of patient trust, and declining revenue, as seen in the case of the 2019 data breach affecting 25 million patients.
How do healthcare organizations ensure compliance with HIPAA when using third-party vendors?
Organizations must vet third-party vendors thoroughly, enter into contractual agreements, and conduct regular compliance audits to ensure that third-party vendors are adhering to HIPAA security standards.
What measures can healthcare providers take to mitigate insider threats?
Providers should establish access controls, conduct employee training programs, and use monitoring systems to detect and prevent unauthorized access or accidental mishandling of data.
How does the growth of telehealth services impact payment security?
Telehealth expansion increases the volume of electronic transactions, which requires safe data transmission protocols, such as end-to-end encryption, for the protection of patient data in consultations and payments.
What makes secure payments systems a strategic investment for healthcare providers?
Beyond compliance, secure payments systems foster patient trust, protect against costly breaches, and enable healthcare providers to focus on delivering quality care without compromising sensitive information.













