In a world where digital transformation is redefining industries, healthcare stands at a critical crossroads. The ability to share, access, and understand patient data across systems and organizations can significantly impact the quality of care. Yet, true interoperability remains elusive for many. The lack of seamless communication between hospitals, clinics, and third-party providers leads to fragmented care, repeated tests, and inefficiencies. The question then arises—how can we improve interoperability in healthcare?
To answer that, we must understand the technical and practical challenges—and the modern solutions like a FHIR-compliant interoperability solution—that are reshaping the healthcare ecosystem.
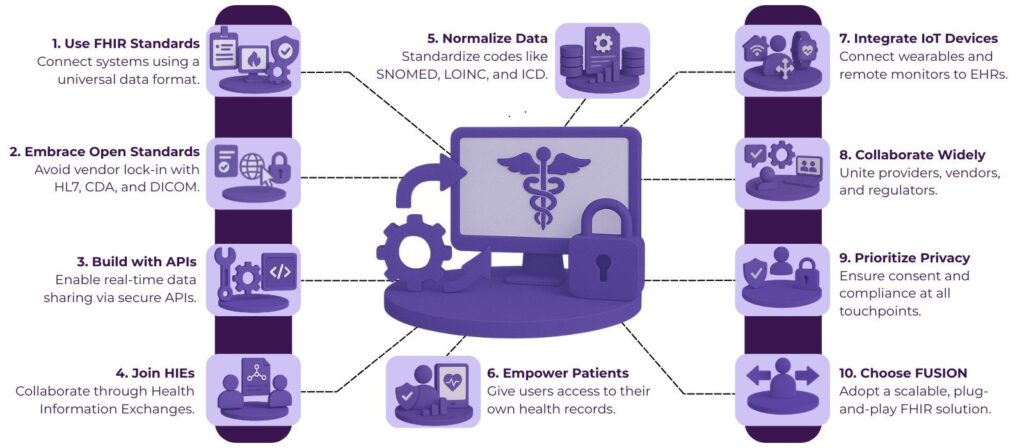
Table of Contents
What Is Interoperability in Healthcare?
Interoperability refers to the ability of different information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, integrate, and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner. In healthcare, this means connecting various electronic health record (EHR) systems, diagnostic tools, insurance databases, and more.
But interoperability isn’t just about technology—it’s about patient-centered care. Imagine a patient visiting a cardiologist who can instantly access their general physician’s notes, lab results, and medication history. That’s the ideal vision. Achieving this, however, requires overcoming deep-rooted silos.
Why Is Healthcare Interoperability Still a Challenge?
Despite advancements in health IT, several obstacles continue to hamper progress:
1. Data Silos Across Organizations
Healthcare providers often use different systems from different vendors. These systems don’t naturally “talk” to each other, which leads to fragmented data silos.
2. Proprietary Standards
Many legacy EHR systems use proprietary data formats, making cross-platform communication nearly impossible without custom integration work.
3. Lack of Incentives
Interoperability requires collaboration across competing institutions. Without financial or regulatory motivation, organizations may deprioritize data sharing.
4. Privacy & Security Concerns
Strict privacy laws, such as HIPAA, add complexity to the process. Therefore, organizations fear breaches and often lean toward caution when sharing patient data.
Key Strategies to Improve Interoperability in Healthcare
Now that we’ve outlined the issues, let’s explore practical and scalable solutions to address them—especially through the lens of FHIR-compliant interoperability.
1. Adopt a FHIR-Compliant Interoperability Solution
The Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard has become the backbone of modern healthcare data exchange. Developed by HL7, FHIR uses modern web-based technologies like REST APIs and JSON/XML formats, making it easier for different systems to share structured data.
A FHIR-compliant interoperability solution allows EHR systems, mobile health apps, and analytics platforms to communicate efficiently. It acts as a universal translator for healthcare data, enabling seamless exchange even across heterogeneous environments.
Benefits of FHIR-Compliant Solutions
- Supports real-time data access via APIs
- Reduces integration time and cost
- Promotes patient access to their own data
- Standardizes how healthcare systems interact
Implementing such a solution helps organizations move from isolated systems to a unified, data-rich ecosystem.
2. Promote the Use of Open Standards
Beyond FHIR, embracing open standards like HL7 v2, CDA (Clinical Document Architecture), and DICOM for imaging data can expand interoperability. Open standards prevent vendor lock-in and create a level playing field where innovation thrives.
Organizations that choose open over proprietary solutions are better positioned to expand their digital health capabilities in the future.
3. Implement API-Driven Architectures
API-first designs are revolutionizing industries—and healthcare is no exception. Rather than relying on batch file transfers or manual data entry, modern systems can use RESTful APIs to pull real-time data from various sources.
FHIR healthcare interoperability heavily relies on this approach. By enabling granular, secure access to patient data, APIs empower providers to make faster, more informed decisions.
Key Benefits
- On-demand access to clinical and administrative data
- Scalability for growing data volumes
- Easier integration with wearable tech and mobile apps
4. Encourage Health Information Exchanges (HIEs)
Health Information Exchanges act as intermediaries, allowing healthcare organizations in a region to share patient information. With proper governance and standardized formats, HIEs facilitate better coordination of care.
To supercharge their utility, integrating HIEs with a FHIR-compliant interoperability solution can make data sharing more dynamic and accessible, especially during emergencies.
5. Invest in Data Mapping and Normalization
Even with FHIR, data won’t be useful unless it’s accurate and meaningful. That’s where data mapping and normalization play a critical role. Terminologies like SNOMED CT, LOINC, and ICD must be correctly mapped to standard codes.
A good interoperability strategy includes tools or middleware that normalize incoming data so that clinicians receive standardized, easy-to-interpret information—regardless of the originating system.
6. Focus on Patient-Centered Interoperability
Patients today want access to their health data. The rise of patient portals and mobile apps makes this possible—but only if backend systems are interoperable.
With a FHIR-compliant interoperability solution, developers can create apps that allow patients to:
- View test results
- Schedule appointments
- Monitor chronic conditions
- Share data with family or providers
This shift puts patients at the center of care while reducing administrative burdens on clinics.
7. Enable Interoperability Across Devices and IoT
With the growing use of wearable devices, at-home monitors, and smart implants, interoperability must extend beyond EHRs.
For example, a FHIR healthcare interoperability setup can integrate real-time glucose levels from a smart insulin pump into a patient’s digital health record. This opens the door to remote monitoring, proactive care, and improved outcomes.
8. Collaborate Across the Ecosystem
No single stakeholder can solve the interoperability challenge. Providers, payers, tech vendors, government agencies, and patients must collaborate.
Participation in industry groups and HL7 accelerators can provide frameworks and playbooks for achieving interoperability at scale.
What Makes FHIR-Compliant Interoperability Solution FUSION Effective?
FUSION, a FHIR-compliant solution by Helixbeat, offers:
- Smart data routing: Routes requests to the right systems in real-time
- Consent management: Allows patients to control who can access their data
- Audit trails: Maintains logs for regulatory compliance
- Plug-and-play APIs: Easily integrates with existing infrastructure
- Scalability: FUSION grows well with evolving needs.
Final Thoughts
We’re only scratching the surface of what interoperability can do. As AI becomes more embedded in clinical workflows, seamless data exchange will become even more important. Predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and remote care delivery all rely on timely access to accurate data.
From startups building health apps to national health schemes, the adoption of FHIR is gaining momentum worldwide. Experience the future of healthcare interoperability today with FUSION.
FAQs
1. What is a FHIR-compliant interoperability solution?
It is a system built on the FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standard that enables different healthcare applications to exchange data easily using modern web technologies.
2. Can patients access their health data through FHIR solutions?
Yes, FHIR-based systems often power patient portals and mobile apps that let patients view and share their medical records securely.
3. What role do APIs play in healthcare interoperability?
APIs allow different systems to communicate directly and on-demand, enabling real-time data exchange and integration with new digital health tools.
4. What are some key features to look for in a FHIR-compliant interoperability solution?
Look for smart data routing, consent management, audit trails, and easy integration with existing healthcare systems.
5. How does FHIR improve healthcare data exchange?
FHIR uses APIs and standardized data formats to provide real-time, structured, and secure access to health information across diverse systems.
6. What challenges prevent healthcare interoperability today?
Common challenges include data silos, proprietary data formats, lack of collaboration incentives, and concerns over data privacy and security.













