Today, interoperability is more than just a buzzword; it’s critical for seamless patient care and operational efficiency. With the ever-growing volume of healthcare data generated daily, the ability to share and utilize information across diverse systems, applications, and organizations has become necessary. In this blog, let’s discuss the challenges, solutions, and real-world examples of healthcare interoperability, and understand why it is so significant for the future of patient care.
Table of Contents
Understanding Interoperability in Healthcare
Healthcare interoperability refers to the ability of different information devices, systems, and applications to access, exchange, and use data in a coordinated manner. It includes not only technical integration but also organizational processes and human workflows. At its core, interoperability aims to provide healthcare professionals with accurate, real-time data to make informed decisions while improving patient outcomes.
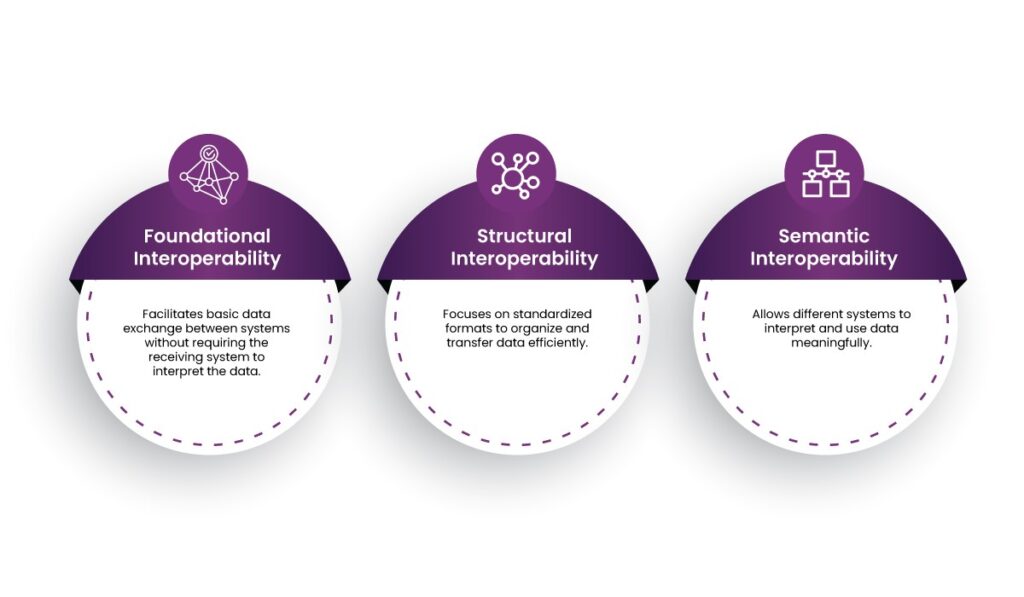
Interoperability operates on three levels:
- Foundational Interoperability: Facilitates basic data exchange between systems without requiring the receiving system to interpret the data.
- Structural Interoperability: Focuses on standardized formats to organize and transfer data efficiently.
- Semantic Interoperability: Allows different systems to interpret and use data meaningfully.
Challenges in Achieving Healthcare Interoperability
Despite its significance, healthcare interoperability faces several barriers that make its implementation difficult. Let’s dive into some of the key challenges:
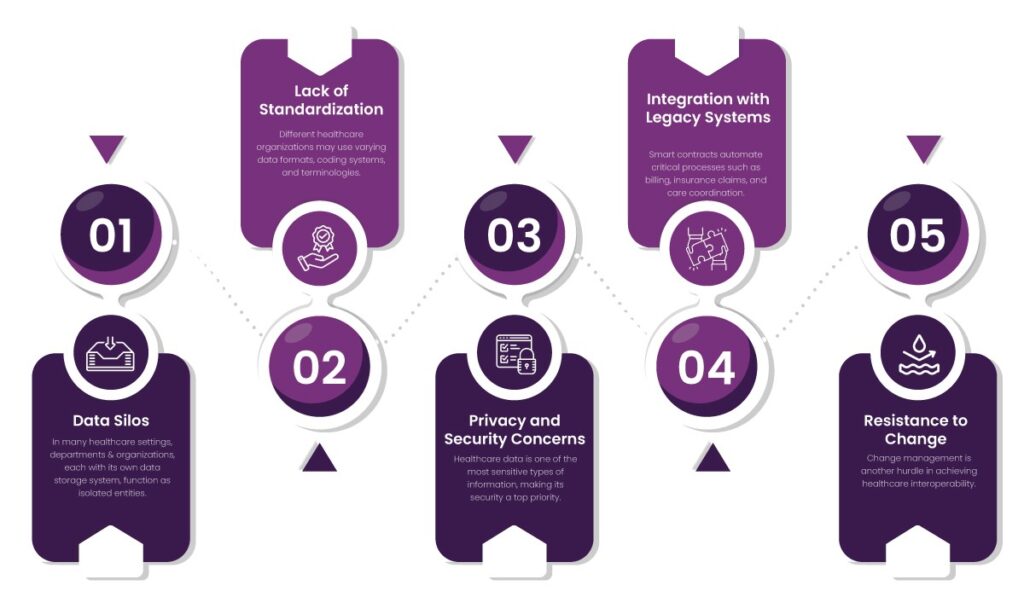
1. Data Silos
In many healthcare settings, departments and organizations, each with its own data storage system, function as isolated entities. These data silos prevent the seamless exchange of information. For example, a patient who underwent blood tests at a diagnostic center may have to undergo the same tests again at a hospital due to inaccessible records.
Therefore, breaking down these silos requires robust data-sharing frameworks that prioritize accessibility without compromising security.
2. Lack of Standardization
Different healthcare organizations may use varying data formats, coding systems, and terminologies.
- Data formats: XML, JSON, or proprietary formats
- Coding systems: ICD-10, SNOMED CT, or CPT
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) software: Cerner, Epic, or smaller regional solutions
This diversity complicates data integration and interpretation.
3. Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare data is one of the most sensitive types of information, making its security a top priority. However, sharing this data across systems amplifies the risk of:
- Data breaches: Cyberattacks on healthcare systems are rising, with patient records becoming valuable targets for malicious actors.
- Unauthorized access: When multiple systems handle patient information, the chances of mishandling increase.
To address this, organizations must implement encryption protocols, robust authentication mechanisms, and data anonymization techniques to mitigate risks.
4. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many healthcare providers still rely on legacy systems that were never designed for interoperability. These systems:
- Lack modern APIs for data exchange.
- Use outdated programming languages and architectures.
For example, a rural clinic might use decades-old software that can’t communicate with modern cloud-based solutions.
5. Resistance to Change
Change management is another hurdle in achieving healthcare interoperability. Healthcare staff and administrators may resist adopting new systems due to:
- Fear of job redundancy.
- Learning curves associated with new technologies.
- Concerns about workflow disruption.
Building a culture that embraces innovation and highlights the benefits of interoperability can help mitigate resistance.
Solutions to Interoperability Challenges
Overcoming these barriers demands a multi-faceted approach that involves technological innovation, collaboration, and policy reform. Here are some solutions to address healthcare interoperability challenges:
1. Adopting Standardized Frameworks
Adopting standardized frameworks, such as HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), facilitates consistent data exchange across platforms. Healthcare interoperability solution AERIS is built on the globally recognized interoperability standard HL7 FHIR, which facilitates consistent and structured data exchange across different Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
2. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud technology provides a scalable and cost-effective platform for data sharing and storage. By leveraging cloud-based systems like AERIS, healthcare providers can access patient data anytime and anywhere, thus facilitating real-time collaboration.
3. Robust Data Governance Policies
Establishing robust data governance policies helps organizations maintain data quality, security, and compliance. AERIS employs a robust framework to safeguard healthcare data through advanced security measures and regulatory adherence. It utilizes:
- Encryption protocols such as AES and TLS to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest.
- Comprehensive access controls, including role-based and context-aware policies, restrict system access to authorized personnel based on their responsibilities, location, and device.
- Detailed audit trails meticulously log every user interaction and system event.
Additionally, AERIS aligns with global standards like HIPAA, thus enabling healthcare organizations to manage patient information responsibly while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
4. Collaborative Efforts
Collaboration among stakeholders—healthcare providers, technology vendors, and policymakers—is crucial for developing interoperable solutions. AERIS expands its integration capabilities by enabling collaboration between healthcare providers, insurance companies, pharmacies, and public health agencies.
5. Patient-Centered Approaches
Empowering patients with access to their health records boosts transparency and engagement. Patient portals and mobile applications enable individuals to manage their health information and share it with multiple providers as needed.

Real-world examples of Healthcare Interoperability
To illustrate the true potential of interoperability, here are some examples of how it has been successfully implemented in healthcare settings:
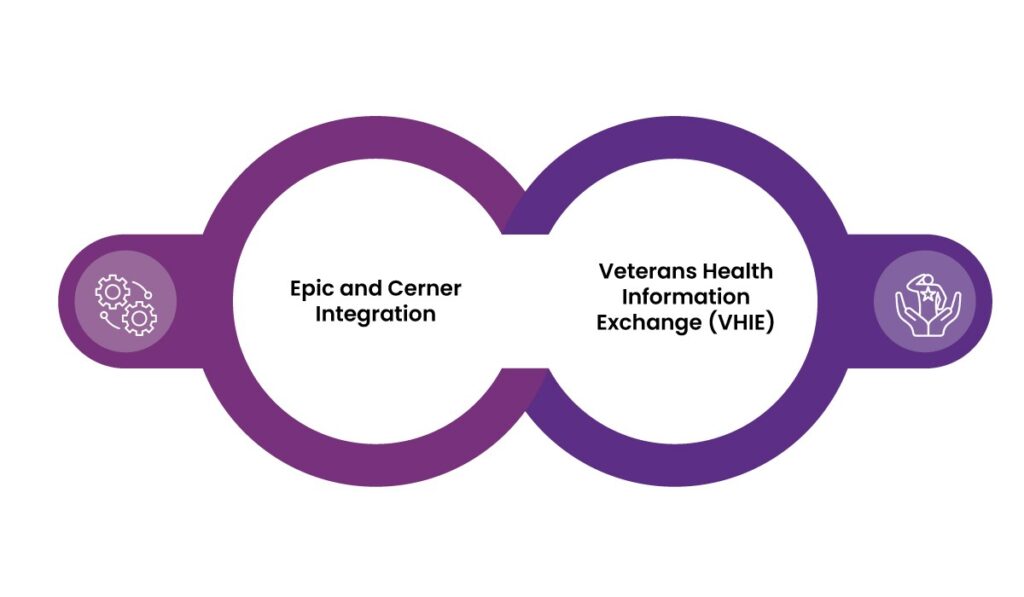
1. Epic and Cerner Integration
Epic and Cerner, two leading EHR providers, have made efforts to improve interoperability between their systems. This includes initiatives to facilitate data exchange for specific use cases, such as patient referrals and emergency care.
2. Veterans Health Information Exchange (VHIE)
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) implemented the VHIE program to connect its healthcare facilities with external providers. This initiative allows VA clinicians to access comprehensive patient records and improve care coordination for veterans.
The Road Ahead
While significant progress has been made, achieving full interoperability in healthcare requires ongoing effort. Policymakers must prioritize initiatives that promote standardization, data security, and technological advancement. Additionally, creating a culture of collaboration and innovation among stakeholders will pave the way for a connected healthcare ecosystem.
HelixBeat is leading this transformation by driving advancements in interoperability and empowering healthcare providers with data-driven insights. If you want to join the journey toward a truly connected healthcare future, explore how AERIS and HelixBeat can help your organization achieve interoperability, enhance efficiency, and deliver better patient outcomes. Reach out to us today and be part of the change that transforms healthcare for the better.
FAQs
1. What is healthcare interoperability, and why is it important?
Healthcare interoperability refers to the ability of different devices, systems, and applications to access, exchange, and use data in a coordinated way. It’s important for improving patient outcomes, facilitating real-time decision-making, and optimizing healthcare operations.
2. What are some major challenges to achieving interoperability in healthcare?
Common challenges include data silos, lack of standardization, privacy and security concerns, integration with legacy systems, and resistance to change.
3. How does AERIS address data security concerns in healthcare?
AERIS employs advanced encryption methods like AES and TLS, role-based and context-aware access controls, and detailed audit trails to safeguard sensitive healthcare data during storage and exchange.
4. What role do standardized frameworks like HL7 FHIR play in interoperability?
Standardized frameworks like HL7 FHIR provide a common structure for data exchange. This makes it easier for diverse systems to share and interpret information.
5. How can cloud-based solutions improve interoperability?
Cloud-based systems offer scalable and cost-effective platforms for real-time data sharing. Therefore, it enables healthcare providers to access patient information anytime and from any location.
6. What are the benefits of breaking down data silos in healthcare?
Eliminating data silos enhances care coordination, reduces redundant tests, speeds up diagnosis, and enables comprehensive access to patient history across healthcare facilities.














