Today, interoperability in healthcare is a make-or-break factor for efficient, error-free patient care. When medical data is scattered across different providers and systems, critical information can slip through the cracks and lead to miscommunication, delays, or compromised outcomes. However, the rise of Electronic Health Record (EHR) software has changed this landscape by streamlining data exchange and bridging gaps between healthcare professionals.
In this blog, we’ll discuss how EHR software strengthens interoperability, improves care coordination, and supports compliance with industry standards—ultimately shaping a more connected and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
Table of Contents
What is Interoperability in Healthcare
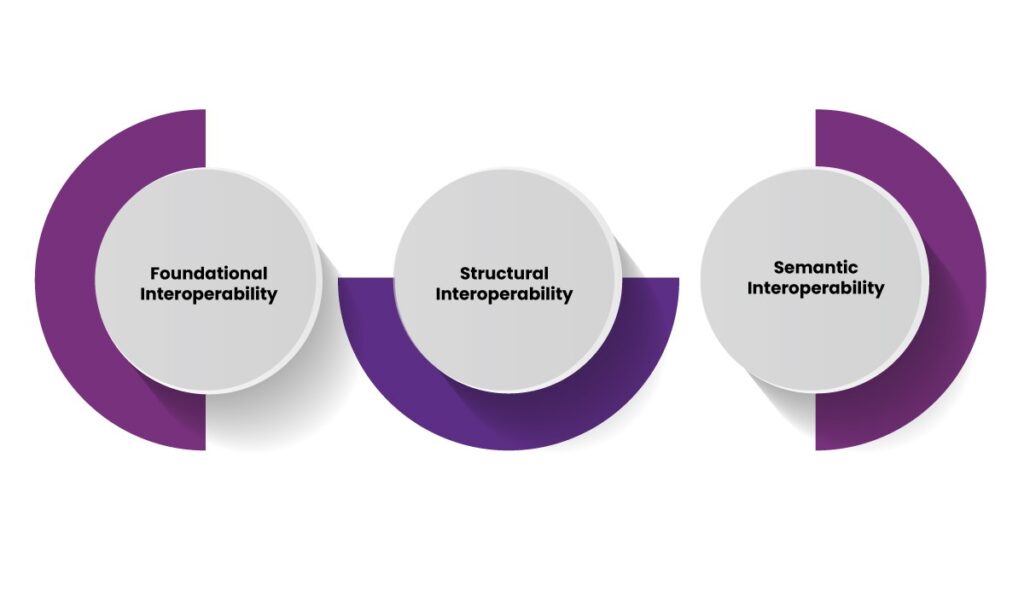
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of different information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, integrate, and cooperatively use healthcare data. It supports timely and informed decision-making by facilitating seamless patient data flow across various healthcare settings. Interoperability can be categorized into three levels:
- Foundational Interoperability – The fundamental ability of one system to send and receive data from another.
- Structural Interoperability – The standardized format and structure of exchanged data lead to proper interpretation.
- Semantic Interoperability – The highest level, where different systems understand and use the exchanged data in a meaningful way.
The Role of EHR Software in Enhancing Interoperability
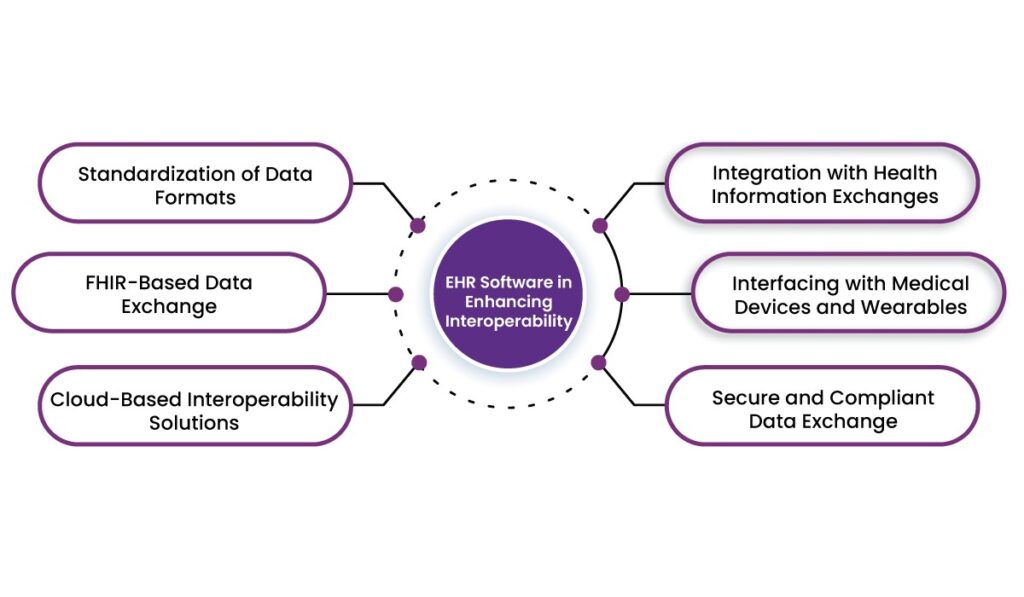
EHR software plays a critical role in overcoming interoperability challenges by integrating healthcare data across various platforms and stakeholders. Below are key ways in which EHR software enhances interoperability:
1. Standardization of Data Formats
One of the fundamental barriers to interoperability is the lack of standardized data formats across different healthcare providers. Modern EHR systems utilize globally recognized data standards such as HL7 (Health Level Seven), FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), and others for consistent data structuring. These standards help healthcare providers to share data seamlessly, regardless of the software vendor or platform.
2. FHIR-Based Data Exchange
FHIR is revolutionizing interoperability by allowing secure, real-time data exchange between healthcare applications. EHR software like PULSE incorporates FHIR APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to facilitate standardized data sharing among hospitals, clinics, and third-party applications. Therefore, PULSE makes it possible for different systems to communicate without extensive custom integration efforts.
3. Cloud-Based Interoperability Solutions
Cloud-based EHR software provides centralized data storage and access, which reduces the silos created by legacy on-premise systems. These platforms allow multiple stakeholders, including primary care providers, specialists, laboratories, and pharmacies, to access real-time patient records securely. Also, cloud computing enhances interoperability by offering flexible and scalable data-sharing solutions without requiring extensive IT infrastructure investments.
4. Integration with Health Information Exchanges (HIEs)
Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) facilitate the secure transfer of patient information across different healthcare entities. EHR software like AERIS can seamlessly integrate with regional and national HIEs and facilitate improved care coordination by providing a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history. This reduces redundant tests, improves treatment accuracy, and enhances the overall quality of care.
5. Interfacing with Medical Devices and Wearables
The rise of wearable health devices and remote monitoring technologies has added a new dimension to healthcare interoperability. EHR software now includes integrations with devices such as smartwatches, blood glucose monitors, and telehealth platforms. This ensures that real-time patient data is automatically recorded in the EHR, thus allowing healthcare providers to track patient conditions remotely and make data-driven decisions.
6. Secure and Compliant Data Exchange
Interoperability must be achieved while maintaining compliance with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA in the U.S. EHR software like AERIS, PULSE, and FUSION incorporates robust security features, including data encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails, to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of patient information.
Benefits of EHR-Enabled Interoperability
EHR-driven interoperability brings numerous benefits to patients, healthcare providers, and the overall healthcare ecosystem. Some key advantages include:
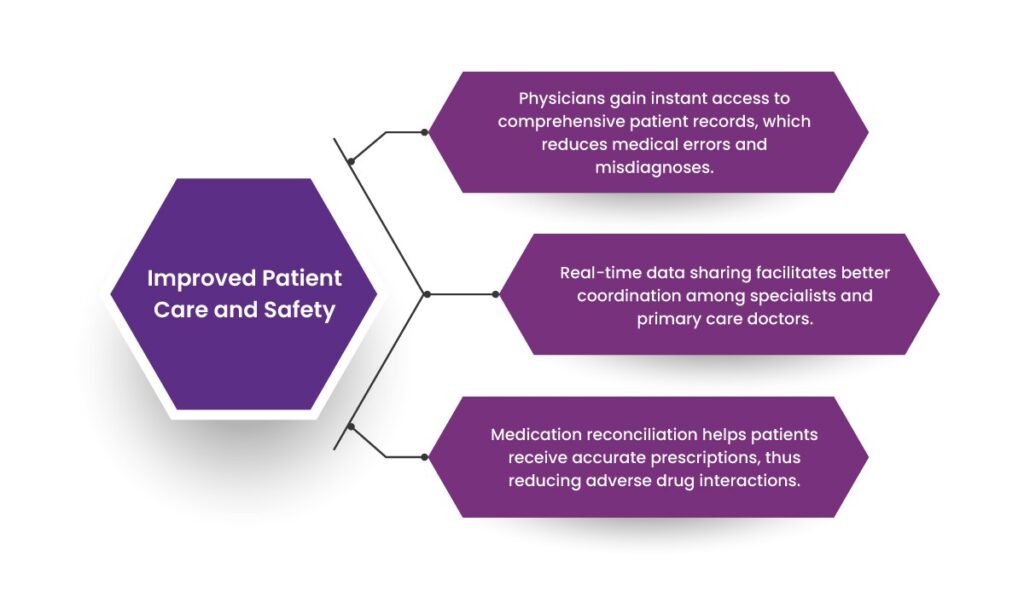
1. Improved Patient Care and Safety
- Physicians gain instant access to comprehensive patient records, which reduces medical errors and misdiagnoses.
- Real-time data sharing facilitates better coordination among specialists and primary care doctors.
- Medication reconciliation helps patients receive accurate prescriptions, thus reducing adverse drug interactions.
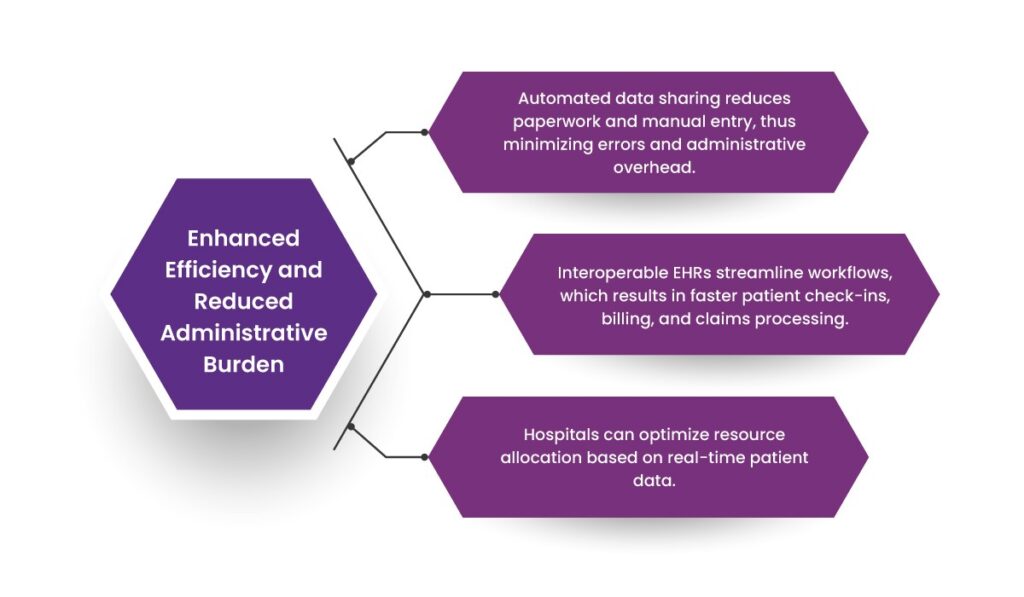
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Reduced Administrative Burden
- Automated data sharing reduces paperwork and manual entry, thus minimizing errors and administrative overhead.
- Interoperable EHRs streamline workflows, which results in faster patient check-ins, billing, and claims processing.
- Hospitals can optimize resource allocation based on real-time patient data.
3. Cost Savings and Revenue Growth
- Interoperability reduces duplicate tests or procedures and lowers unnecessary healthcare costs.
- Real-time insurance eligibility verification improves billing accuracy and accelerates reimbursements.
- Data-driven insights from EHR software facilitate better patient population management.
Future Trends in EHR Interoperability
With ongoing technological advancements and regulatory initiatives, the future of EHR interoperability looks promising. Some emerging trends include:
- DLT for Secure Health Data Exchange: Distributed ledgers like PULSE enhance security and data integrity.
- Interoperability Mandates: Governments worldwide are pushing for greater standardization and open API requirements.
- 5G-Enabled Healthcare: Faster connectivity will support real-time data sharing and remote patient monitoring.
- AI-Driven Interoperability Solutions: Predictive analytics will help anticipate patient needs and optimize care delivery.
Final Words
EHR software has transformed healthcare interoperability by enabling seamless data exchange, enhancing patient care, and improving operational efficiency. By leveraging standardized data formats, FHIR-based APIs, cloud integration, and AI-powered analytics, modern EHR systems make sure that patient information is accessible and actionable across different healthcare settings. While challenges remain, ongoing innovations and policy initiatives will continue to drive improvements in interoperability, ultimately benefiting both patients and providers.
Therefore, adopting interoperable EHR systems is not just a technological upgrade but a fundamental shift toward a more connected, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare ecosystem. As the industry moves forward, embracing emerging technologies and standardized frameworks will be key to realizing the full potential of EHR-driven interoperability.
FAQs
1. Why is interoperability important in healthcare?
Interoperability enhances communication between healthcare providers, reduces medical errors, improves treatment coordination, and minimizes redundant tests. It also helps maintain comprehensive patient records, which leads to better health outcomes.
2. How does EHR software improve interoperability?
EHR software improves interoperability by adopting standardized data formats like HL7 and FHIR, integrating with Health Information Exchanges (HIEs), enabling cloud-based data sharing, and facilitating secure communication between different healthcare systems.
3. What role do data standards like HL7 and FHIR play in healthcare interoperability?
Data standards like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) create a uniform structure for health data exchange, making it easier for different systems to communicate and interpret patient information accurately.
4. How does cloud-based EHR software contribute to interoperability?
Cloud-based EHR software allows real-time access to patient records from any location, which reduces data silos. It also enhances collaboration among healthcare providers by providing a centralized, secure, and scalable data-sharing environment.
5. How does wearable health technology impact EHR interoperability?
Wearable devices like smartwatches and glucose monitors generate real-time health data that can be integrated into EHR software. This allows healthcare providers to monitor patient conditions remotely and make informed treatment decisions.
6. What security measures are in place to protect interoperable health data?
EHR systems protect patient data using encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA also helps maintain data privacy and security in interoperable healthcare environments.
7. How does interoperability reduce healthcare costs?
Interoperability eliminates duplicate tests, minimizes administrative burden, and improves billing accuracy. By streamlining workflows and enabling better coordination, healthcare facilities can optimize resource allocation and reduce unnecessary expenses.














