The healthcare industry is a complex ecosystem with multiple players—hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, insurers, and diagnostic labs—working toward a common goal: improving patient outcomes. Yet, the lack of seamless communication between these entities often hampers progress. This is where interoperability steps in, revolutionizing healthcare by facilitating the secure and efficient exchange of patient data across systems. The result? Improved patient outcomes and significant cost reductions.
This blog will discuss healthcare interoperability and how it enhances patient care, reduces expenses, and creates a more efficient healthcare system.
Table of Contents
Understanding Interoperability in Healthcare
Healthcare interoperability refers to the ability of different information systems, devices, and applications to communicate and exchange data effectively. With this, healthcare providers can access accurate, up-to-date patient information, regardless of where the data originated.
For example, a patient’s electronic health record (EHR) created in a hospital should be accessible to their general physician, specialists, or even a diagnostic lab. With healthcare interoperability, this information is readily accessible.
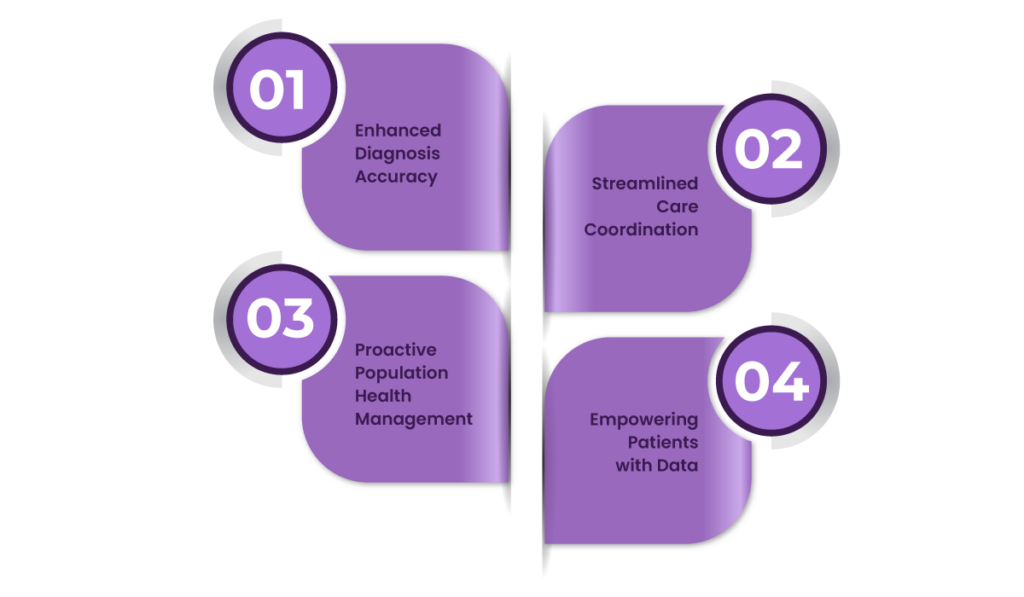
How Interoperability Improves Patient Outcomes
1. Enhanced Diagnosis Accuracy
Interoperability enables healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient records, including medical history, lab results, imaging studies, and prescribed medications, all in one place. This integration eliminates gaps in information that might lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
2. Streamlined Care Coordination
Chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease often require a multi-disciplinary approach. Without healthcare interoperability, coordinating care between primary care physicians, specialists, and therapists becomes cumbersome.
However, healthcare interoperability creates a unified platform where all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care can collaborate effectively. As a result, it improves patient outcomes by reducing the risk of treatment overlaps or conflicting prescriptions.
3. Proactive Population Health Management
On a larger scale, interoperability supports population health management by aggregating data from various sources to identify trends, risk factors, and preventive measures. For example, during a flu outbreak, interoperable systems can track the spread of the virus and facilitate healthcare organizations to roll out vaccination drives efficiently.
This proactive approach reduces hospital admissions and helps communities stay healthier, highlighting how healthcare interoperability directly impacts patient well-being.
4. Empowering Patients with Data
Healthcare interoperability isn’t just for healthcare providers—it empowers patients by giving them access to their own health data through patient portals or apps. When patients are well-informed about their medical history, ongoing treatments, and test results, they are more likely to adhere to prescribed regimens and engage in shared decision-making with their doctors.
For example, wearable devices that sync with electronic health records (EHRs) can provide patients and doctors with real-time updates on vital signs, improving monitoring and reducing emergency visits.
How Interoperability Reduces Healthcare Costs
1. Minimizing Redundant Tests and Procedures
A study estimated that eliminating redundant tests could save the US healthcare system approximately $8 billion annually. When systems fail to communicate, patients often undergo repeated blood tests, imaging studies, or screenings simply because previous results are unavailable to the treating physician.
Healthcare interoperability mitigates this by providing a single repository of patient data accessible to all authorized healthcare providers. This reduces unnecessary expenses and prevents patients from undergoing redundant or invasive procedures.
2. Reducing Administrative Burdens
A 2021 McKinsey report found that streamlining administrative processes in the US healthcare system could save $265 billion annually without compromising quality or access. Healthcare interoperability can simplify administrative tasks like insurance claims processing, appointment scheduling, patient billing, etc. By automating data exchange between providers and payers, healthcare organizations can save time and resources.
For example, pre-authorization for treatments can be completed faster when insurers have direct access to a patient’s relevant medical records. This reduces bottlenecks and allows healthcare staff to focus on patient care rather than paperwork.
3. Preventing Medication Errors
Medication errors are a big source of preventable healthcare costs, often resulting in complications requiring additional treatments or hospitalizations. However, healthcare interoperability prevents this by automatically revealing information about prescribed medications to other providers. This safeguards patient health and reduces costs associated with adverse drug reactions.

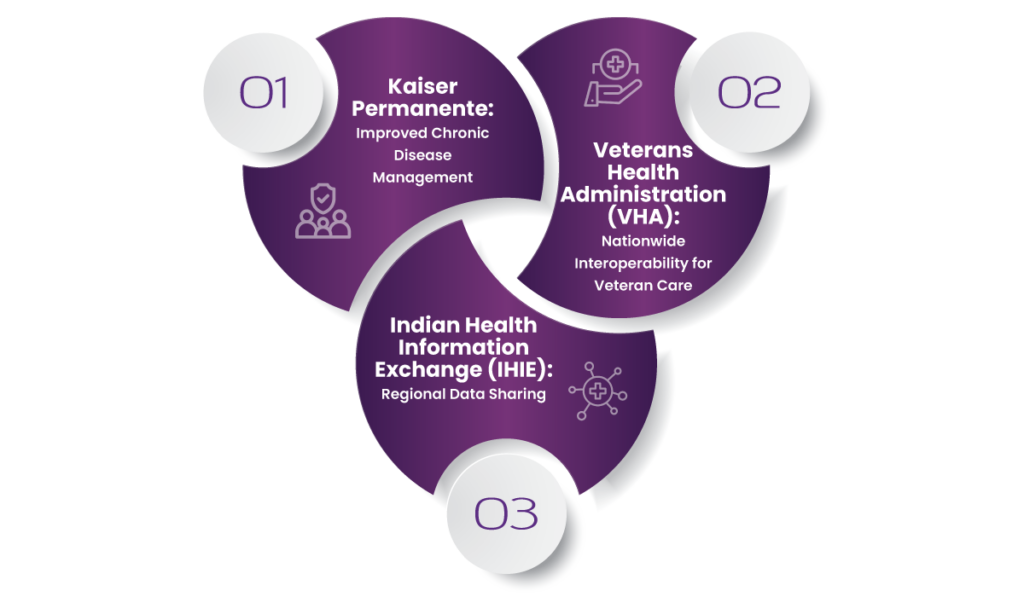
Real-Life Examples of Interoperability Success
1. Kaiser Permanente: Improved Chronic Disease Management
Kaiser Permanente, a leading healthcare provider in the US, leverages interoperability to connect its network of hospitals, clinics, and labs. By integrating data from various sources, Kaiser has significantly improved the management of chronic diseases like diabetes. Based on comprehensive data analysis, patients receive personalized care plans, which result in fewer complications and lower costs.
2. Veterans Health Administration (VHA): Nationwide Interoperability for Veteran Care
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has established one of the US’s most comprehensive interoperable healthcare systems. By integrating its electronic health record (EHR) system with other healthcare providers nationwide, the VHA facilitates seamless data sharing for millions of veterans. Also, veterans who receive care outside the VA network benefit from continuity in treatment because their complete medical history is accessible to external providers.
3. Indiana Health Information Exchange (IHIE): Regional Data Sharing
The Indiana Health Information Exchange (IHIE) is one of the largest and longest-standing health information exchanges (HIEs) in the United States. It connects more than 117 hospitals, healthcare organizations, and clinics across Indiana, allowing providers to share patient data in real-time. IHIE has facilitated the early detection of public health issues and streamlined chronic disease management.
The Future of Interoperability in Healthcare
As technology advances, healthcare interoperability is poised to evolve further, driven by innovations like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). AI-powered analytics will help interpret vast amounts of interoperable data to predict patient outcomes, while blockchain can enhance data security. IoT devices, like remote patient monitoring tools, will further expand the scope of interoperability by integrating real-time data into patient records.
These developments promise a future where healthcare is more efficient, personalized, accessible, and cost-effective.
Final Words
Interoperability is reshaping healthcare by breaking down silos, improving communication, and fostering collaboration. Enhancing diagnostic accuracy, streamlining care coordination, and empowering patients drives better health outcomes. Simultaneously, it reduces healthcare costs by minimizing redundancies, lowering administrative burdens, and optimizing resources.
As the healthcare industry continues to embrace interoperability, its transformative potential will become even more apparent. A future where every patient receives timely, accurate, and cost-effective care is no longer a distant dream but an achievable reality.
FAQs
1. What is healthcare interoperability?
Healthcare interoperability is the ability of different healthcare systems, devices, and applications to effectively communicate and exchange patient data.
2. How does interoperability improve diagnostic accuracy?
Interoperability consolidates a patient’s medical history, lab results, imaging studies, and prescriptions into a unified system. This reduces information gaps that could lead to misdiagnosis or delays in treatment.
3. Why is interoperability important for chronic disease management?
Interoperability facilitates collaboration among healthcare providers, such as primary care doctors, specialists, and therapists, making coordinating care and managing chronic conditions easier.
4. What role does interoperability play in reducing healthcare costs?
By minimizing redundant tests, automating administrative processes, and reducing medication errors, interoperability helps cut unnecessary expenses and improves resource allocation in the healthcare system.
5. How does interoperability empower patients?
Patients gain access to their health data through portals or apps, which helps them stay informed, make better decisions about their treatment, and adhere to prescribed regimens.
6. Can interoperability help during public health crises?
Yes, interoperability enables real-time data sharing, which is critical for tracking disease outbreaks, managing resources, and implementing preventive measures.
7. What future technologies will enhance interoperability?
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and IoT devices are expected to improve further data integration, security, and real-time monitoring in interoperable healthcare systems.













