Visitor tracking has come a long way from its humble beginnings. It all started with simple sign-in sheets and has evolved into today’s sophisticated smart solutions. We are living in an era where security, efficiency, and personalization are crucial. The evolution of visitor management reflects how technology adapts to meet the changing needs of premises and individuals.
Visitor management was born out of necessity—to monitor, record, and control who enters and exits a facility. While early practices were rooted in handwritten logs and manual systems, they laid the foundation for more advanced solutions integrating digital tools, automation, and artificial intelligence. Over the decades, each technological leap has revolutionized how organizations approach visitor management, transforming it from an essential security measure to a seamless and integral part of modern operations.
Today, visitor management systems do more than just track names and times; they play a pivotal role in improving workplace security, ensuring compliance with regulations, enhancing visitor experiences, and even contributing to an organization’s overall efficiency. With the advent of mobile apps, cloud-based systems, and AI-powered solutions, visitor management has become smarter, faster, and more reliable than ever.
This blog will take you on a journey through the fascinating evolution of visitor tracking. We’ll explore its early roots, trace its technological milestones across the decades, and discuss VISTA, a modernized version of visitor management designed for the current era. Finally, we’ll look ahead to the future, imagining the possibilities as visitor management evolves in a world increasingly driven by innovation.
Let’s see the thrilling evolution into how visitor tracking has grown from simple sign-in sheets to cutting-edge innovative solutions, and why it matters in the fast-paced world we live in today.
Table of Contents
Early roots, why and where?
The concept of visitor management has its roots in the basic need for security and accountability. Long before modern systems existed, early societies used rudimentary methods to monitor access to important places. Ancient civilizations like Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Rome employed gatekeepers or guards to control entry into palaces, temples, and administrative centres. Written records, often carved into stone or maintained in ledgers, served as the first “visitor logs.”
The purpose was simple: to ensure that only authorized individuals could access sensitive or sacred areas. As societies became more structured, this need expanded to include businesses, estates, and government offices. By the 18th and 19th centuries, the Industrial Revolution further highlighted the importance of visitor tracking. In rapidly growing industrial hubs like England and Germany, factories and administrative offices started keeping physical logbooks to document visitors.
These early systems emerged to address practical concerns such as preventing theft, ensuring worker safety, and maintaining operational control. They were entirely manual and relied on human oversight, making them prone to errors and inefficiencies.
While rudimentary, these methods laid the foundation for today’s sophisticated visitor management systems, emphasizing the timeless need for monitoring, security, and accountability in every era.
The Beginnings: 19th and Early 20th Century—Manual Records
The 19th and early 20th centuries marked the formalization of visitor management as societies became more organized, industrialized, and interconnected. This era relied heavily on manual systems to track visitors, with physical logbooks as the backbone of visitor management. Factories, offices, government institutions, and private estates adopted these methods to document who entered and exited their premises.
Industrial hubs like England and Germany were at the forefront of visitor tracking practices during this period. Factories must monitor workers, visitors, and suppliers to maintain safety and prevent theft. Similarly, government offices and aristocratic estates implemented logbooks to maintain order, ensure accountability, and restrict unauthorized access.
These manual records were straightforward: visitors wrote their names, the purpose of their visit, the person they intended to meet, and the time of arrival. Though simple, the process was labour-intensive and prone to errors. Lost or illegible entries could need clarification, and there was no quick way to retrieve past records.
Despite their limitations, these manual systems fulfilled the security and administrative needs of the time. They also introduced the concept of visitor accountability, ensuring that each individual entering a facility left behind a traceable record.
As industries grew and workplaces became more complex, the shortcomings of manual systems became apparent. The need for faster, more reliable methods of managing visitors began to emerge, paving the way for technological advancements in visitor tracking.
Although this era may have been rudimentary, it established key principles of visitor management that remain relevant today: accountability, security, and record-keeping. These principles would evolve with the advent of new technologies, transforming visitor management into the sophisticated systems we know today.

1950s-1970s: Security-Driven Evolution
The mid-20th century marked a significant shift in visitor management, mainly driven by growing concerns about security and privacy. During this era, businesses, government organizations, and institutions began to prioritize controlling access to their premises, particularly in response to geopolitical tensions and industrial espionage. This period saw the transition from essential record-keeping to more structured systems focused on safety and security.
The Cold War heightened the need for stringent visitor tracking, especially in sensitive locations like government buildings, defence establishments, and research facilities. Sign-in sheets were supplemented with additional measures such as identification checks, badges, and restricted access areas. For example, visitors were often required to display temporary ID badges to signify their authorization and ensure accountability.
In corporate environments, the rise of administrative protocols during the 1950s and 1960s prompted a shift in how businesses approached visitor management. Reception desks became the central point for visitor tracking, where staff manually logged information and issued identification tags to streamline access control.
By the 1970s, organizations started implementing basic mechanical and electronic systems to enhance security. Innovations such as time-stamped entry records and numbered badge systems were introduced, reducing reliance on manual logs and improving accuracy. Facilities with high-security needs, such as military bases and laboratories, began using locked entry gates operated by guards or keycards, hinting at future digital transformations.
This era established a culture of proactive security in visitor management. It highlighted the need to balance hospitality with safety, which remains essential today. These advances laid the groundwork for the technological innovations of the 1980s, when digital solutions began to replace manual systems, further elevating visitor management practices.

1980s: Digital Beginnings
The 1980s marked a turning point in visitor management as organizations began embracing digital technology to address the limitations of manual systems. This decade saw the rise of computers in workplaces, sparking the development of digital visitor-tracking solutions. These innovations aimed to enhance security, streamline processes, and reduce human error.
One of the earliest digital advancements was the introduction of computer-based visitor log systems. Instead of relying solely on physical logbooks, receptionists could now input visitor details into basic software programs. This made organising and retrieving visitor records easier while minimizing the risk of lost or illegible entries. These systems also allowed for time-stamping, making it more accurate to track when visitors arrived and departed.
Large corporations and high-security facilities, such as technology firms and government agencies, were early adopters of these digital systems. For example, some organizations began automating check-ins using barcode scanners and magnetic strip cards. Visitors would be issued ID cards with unique codes that could be scanned to log their entry and exit, ensuring a faster and more secure process.
The 1980s also saw the rise of networked computer systems, enabling organizations to centralize their visitor records. Facilities with multiple entry points could share data in real time, providing a more cohesive approach to visitor management. This was particularly useful for large campuses or multi-building offices where managing visitor flow required greater coordination.
While these systems were rudimentary compared to today’s technology, they marked the beginning of a digital revolution in visitor management. By automating data entry and enhancing record accuracy, they set the stage for more sophisticated solutions in the following decades, from networked systems in the 1990s to the cloud-based platforms of the 2000s.

1990s: Networked Solutions
The 1990s ushered in a new era for visitor management, fueled by the widespread adoption of networked computers and the internet. During this decade, businesses and organizations began leveraging these technologies to create more integrated and efficient visitor tracking systems. The goal was to streamline processes, enhance data accessibility, and improve security measures across multiple locations.
One of the most significant developments was the introduction of networked visitor management software. These systems allowed organizations to centralize visitor data, enabling seamless information sharing across different entry points and locations. For example, a company with offices in multiple cities could now maintain a unified database of visitors, accessible in real-time by authorized personnel. This advancement drastically reduced redundancy and improved accuracy in record-keeping.
Another key innovation was the use of digital ID systems. Organizations started issuing photo badges and smart cards to visitors, which could be scanned or swiped for instant check-ins and check-outs. These systems enhanced efficiency and bolstered security by ensuring that only verified individuals could access certain areas.
The growing popularity of the Internet during this period further expanded visitor management capabilities. Web-based systems began to emerge, allowing organizations to implement online visitor pre-registration. This feature enabled guests to input their details before arriving, reducing wait times and improving the overall experience.
The 1990s also saw visitor management integration with other security systems, such as CCTV cameras and access control. This convergence marked a shift toward a more holistic approach to facility security, where visitor data and surveillance technologies worked in tandem.
By the end of the decade, networked solutions had firmly established visitor management as a critical component of organizational security and operational efficiency, setting the stage for the automation and mobility revolutions of the 2000s.

2000s: The Era of Automation
The 2000s were a transformative phase in visitor management, with automation becoming the driving force behind modernizing processes. As software and hardware technologies evolved rapidly, organizations started adopting automated visitor management systems to improve efficiency, security, and user experience.
Among the outstanding innovations of this era were self-service kiosks. These touch-screen devices enable visitors to check themselves in, input their details, and print temporary ID badges without requiring the intervention of reception staff. This automation minimizes wait times and facilitates a more streamlined check-in process, especially in high-traffic environments such as corporate offices, hospitals, and events.
The software solutions also improved. The new features included email and SMS notifications to alert hosts about the visitor’s arrival. Pre-registration emerged, allowing guests to register their visits online before visiting to accelerate the entry process further.
Visitor management was merged with sophisticated access control technologies in the 2000s and allowed facilities to assign temporary IDs to visitors. Biometric scanners and RFID technology combined further ensured that only authorized places were accessed.
This decade was focused on automation, which improved operational efficiency and set new standards for security and convenience. This paved the way for the mobile and cloud-driven innovations of the 2010s.

2010s: Mobile and Cloud Revolution
The 2010s was a transformative decade for visitor management, with several key innovations and features arising due to the widespread adoption of mobile technology and cloud computing. These innovations significantly enhanced the efficiency, flexibility, and security of visitor tracking systems.
- Mobile Check-In: The ability for visitors to check in using their smartphones became a game-changer. Mobile apps allowed guests to pre-register, scan QR codes upon arrival, and check in digitally, eliminating the need for paper-based logbooks. This made the process faster and more efficient, especially in high-traffic locations.
- QR Code and NFC Integration: QR code scanning and Near Field Communication (NFC) technology enabled contactless check-ins, offering added convenience and reducing physical interactions. Visitors could simply scan a code on their mobile devices or use NFC-enabled badges to gain entry.
- Cloud-Based Systems: Cloud computing revolutionized visitor management by providing a scalable, cost-effective solution. Cloud-based systems offered the flexibility to access data remotely, eliminate on-premises infrastructure, and simplify software maintenance with automatic updates. These systems also enabled real-time data synchronization across multiple locations.
- Pre-Registration: Many visitor management systems in the 2010s introduced online pre-registration, where visitors could submit their details in advance. This reduced wait times and improved guest experience, especially for events or busy office buildings.
- Real-Time Notifications: Systems integrated with email and SMS notification capabilities, alerting hosts when their guests arrived. This feature improved communication and allowed for smoother scheduling.
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics: Cloud systems offered real-time reporting capabilities, allowing administrators to generate insights on visitor trends, security compliance, and occupancy.
- Enhanced Security Features: With increasing concerns about data privacy and security, visitor management systems in the 2010s incorporated advanced features like facial recognition, biometric scanning, and data encryption, improving both physical and data security.

2020s and Beyond: AI and Smart Solutions
The 2020s marked the dawn of the next phase in visitor management, driven by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and smart technology. These innovations are transforming how organizations manage visitors, with a focus on automation, personalized experiences, and enhanced security.
One of the most notable advancements is the integration of AI-driven systems that can predict visitor behavior, streamline check-in processes, and improve resource allocation. AI-powered tools can automate guest identification, verify identities, and even assess visitor risk levels based on past behavior or access patterns.
Facial recognition technology has become a key feature in many modern visitor management systems, allowing for touchless check-ins that enhance both security and convenience. This technology reduces the need for physical ID checks, speeding up the process while ensuring only authorized visitors gain access to restricted areas.
Smart building integration is another crucial development in this era. Visitor management systems now connect with building management systems, adjusting lighting, heating, and access controls in real-time based on visitor activity. This seamless integration enhances both the visitor experience and building efficiency.
Moreover, cloud-based AI solutions enable data analysis to optimize workflows, generate insights for improving security protocols, and enhance overall operational efficiency. As AI technology advances, we can expect even more personalized, secure, and efficient visitor management systems to emerge in the years to com

VISTA: the modernized version of visitor management
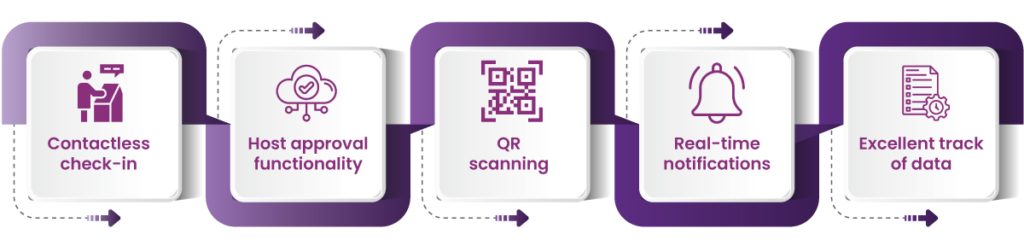
VISTA represents the next generation of visitor management, offering a highly advanced, efficient, and secure solution for modern organizations. Designed to streamline and enhance the visitor experience, VISTA incorporates cutting-edge features that address the evolving needs of businesses today.
One of the standout features of VISTA is contactless check-in, allowing visitors to self-register via their smartphones or kiosks without physical interaction. This minimizes delays, promotes safety, and reduces the need for in-person reception staff, especially in high-traffic environments.
The system also includes host approval functionality, enabling hosts to approve or deny visitors in real time, ensuring that only authorized individuals gain access to the premises. This adds an additional layer of security and control over who enters the building.
VISTA utilizes QR scanning, allowing visitors to quickly check in by scanning a unique QR code sent to their mobile devices or displayed at the entry point. This touchless method speeds up the process and minimizes contact with surfaces, enhancing both efficiency and safety.
With real-time notifications, VISTA keeps hosts informed of their visitor’s arrival instantly, ensuring timely reception. Furthermore, VISTA maintains an excellent track of data, providing detailed records and analytics on visitor patterns, security compliance, and building usage, which can be accessed anytime for audit or reporting purposes.
The Future of Visitor Tracking
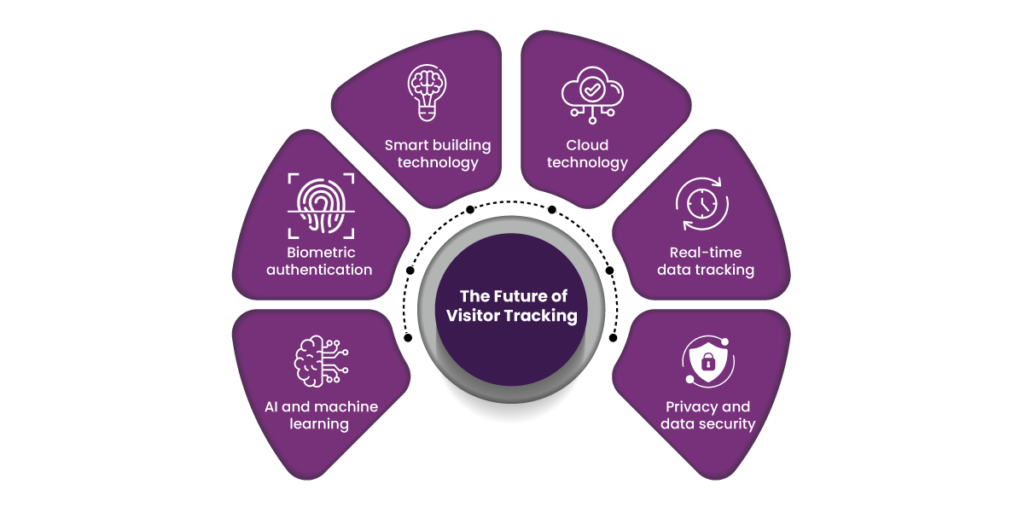
The future of visitor tracking looks incredibly promising, with technology continuing to evolve and introduce more sophisticated, intelligent, and efficient systems. As organizations become more focused on enhancing security, optimizing the visitor experience, and ensuring regulatory compliance, the role of visitor management systems is expected to grow in complexity and capability. The next-generation visitor tracking systems will not only enhance operational efficiency but will also introduce new levels of personalization, automation, and seamless integration with other business systems.
One key trend shaping the future is AI and machine learning. These technologies are likely to play an even larger role in visitor management systems. AI can predict visitor behaviors, identify patterns, and suggest actions based on historical data, which will help organizations better prepare for the volume of visitors, anticipate security risks, and streamline operations. Machine learning algorithms can continuously improve system efficiency by analyzing visitor data and learning from past interactions to optimize the check-in and check-out processes.
Biometric authentication is another area that will continue to gain traction. While facial recognition technology is already in use, we can expect even more advanced biometric systems, including iris and fingerprint recognition, to become more widespread. These systems will offer a higher level of security by ensuring that only authorized individuals are allowed access, while also speeding up the check-in process by eliminating manual entry.
As more businesses embrace smart building technology, visitor management systems will integrate more seamlessly with building systems to enhance both visitor experience and operational efficiency. From controlling room temperature and lighting to optimizing elevator usage based on visitor traffic, smart buildings will be better equipped to handle the complex needs of visitors and employees. Organizations will create a more comfortable and efficient environment for everyone involved by automating these processes.
Cloud technology will continue to be essential in visitor tracking. Cloud-based systems are already widely used for storing and managing data, and their benefits—such as remote access, scalability, and ease of updates—are expected to remain a cornerstone of future solutions. Additionally, cloud systems will allow for better collaboration across multiple locations, enabling organizations to manage visitors at scale, regardless of geographical boundaries. This is particularly beneficial for global enterprises with offices in multiple regions.
Real-time data tracking will also become a more significant feature in future systems. With advanced analytics, visitor management solutions will offer in-depth insights into visitor trends, peak times, and security risks. Organizations will be able to make data-driven decisions on optimising space utilisation, enhancing security protocols, and improving customer service. This real-time data collection can also be integrated with other enterprise systems like customer relationship management (CRM) tools, allowing for more personalized experiences and more efficient management of corporate resources.
Furthermore, the emphasis on privacy and data security will grow stronger. As data breaches and cybersecurity threats increase, visitor management systems will incorporate more advanced encryption methods, ensuring that personal and sensitive information is well-protected. Compliance with various regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), will continue to be a key priority, with systems evolving to meet the growing data handling and storage requirements.
Conclusion
The evolution of visitor tracking has come a long way, from manual sign-in sheets to sophisticated, AI-powered solutions that offer seamless, efficient, and secure visitor management. As technology advances, visitor management’s future will be defined by a stronger focus on automation, personalization, and integration with other business systems. Visitor management systems will not just be tools for tracking who enters a building but will evolve into comprehensive solutions that enhance operational efficiency, improve security, and optimize the overall visitor experience.
In the coming years, organizations can expect to see even more intelligent systems powered by AI and machine learning, integrated biometric authentication for smoother and more secure check-ins, and better data-driven insights that allow businesses to optimize their visitor management processes in real-time. Moreover, as the world becomes more connected, integrating visitor management with innovative building technologies and cloud platforms will make it easier to manage visitors at scale, regardless of location.
Overall, the future of visitor tracking will be defined by more innovative, more secure, and more efficient systems that provide both operational and experiential benefits to organizations and visitors alike.
FAQs
- What is a visitor management system?
A visitor management system is a digital solution designed to monitor, track, and manage visitors entering and exiting a facility. It enhances security, streamlines check-in processes, and ensures accurate visitor records.
- How does a visitor management system improve security?
It verifies visitor identities, restricts unauthorized access, integrates with access control systems, and provides real-time monitoring of visitor activities.
- Can visitor management systems integrate with other security tools?
Yes, modern systems often integrate with access control, surveillance cameras, biometric scanners, and alarm systems for a holistic security approach.
- What industries benefit most from visitor management systems?
Industries such as corporate offices, healthcare, education, manufacturing, government facilities, and events benefit greatly from visitor management systems.
- Are visitor management systems customizable?
Many systems offer customizable features, such as branding, visitor categories, host notifications, and pre-registration forms, to meet specific organizational needs.
- How does a visitor management system handle data privacy?
Advanced systems comply with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA, encrypt sensitive information, and provide options for secure data storage and access.
- What are self-service kiosks, and how do they work?
Self-service kiosks are touch-screen devices where visitors can check in, input their details, and print badges independently, reducing reliance on reception staff.
- Can visitor management systems support multiple locations?
Yes, cloud-based systems can centralize data across multiple locations, providing unified visitor tracking and reporting.
- What is pre-registration, and how does it work?
Pre-registration allows visitors to input their details online before arriving, speeding up the check-in process and notifying hosts of their expected arrival.
- Do visitor management systems work with mobile devices?
Yes, many systems offer mobile apps or QR-code-based check-ins for visitors to complete their registration using smartphones.
- What features should I look for in a visitor management system?
Key features include digital check-in, visitor pre-registration, ID badge printing, access control integration, real-time alerts, and reporting capabilities.
- How is visitor information stored and accessed?
Information is stored in secure databases, often cloud-based, and can be accessed by authorized personnel for reporting or compliance purposes.
- Can visitor management systems handle large events?
Yes, event-specific features like bulk pre-registration, badge printing, and streamlined check-ins are designed to manage high visitor volumes efficiently.
- How do notifications work in visitor management systems?
Notifications are sent via email, SMS, or app alerts to inform hosts about their visitors’ arrival or unexpected events during the visit.
- What are the benefits of using a cloud-based visitor management system?
Cloud-based systems offer scalability, real-time data access, multi-location integration, and remote management, ensuring flexibility and convenience.












