Imagine a patient’s complete medical history—lab results, prescriptions, and treatment plans—flows seamlessly between healthcare providers. Now, picture that same data falling into the wrong hands. Today, cybercriminals aren’t just after credit card numbers anymore; they’re targeting medical records, which fetch a higher price on the black market. As reported by the Infosec Institute, the market value of stolen patient health records can reach $363 per record. Therefore, securing healthcare data transfers is more than a compliance checkbox—it’s a mission-critical priority.
In this blog, we’ll explore the role of encryption in securing data, the impact of regulatory frameworks on healthcare data transfers, and strategies organizations must adopt to keep patient information safe.
Table of Contents
The Role of Encryption in Securing Healthcare Data Transfers
Why Encryption is Non-Negotiable
Encryption transforms data into a format that only authorized parties can decipher. This prevents unauthorized access, even if the data is intercepted during transmission. Healthcare organizations leverage encryption to protect electronic health records (EHRs), insurance details, and other confidential information shared between hospitals, clinics, and insurers.
Types of Encryptions Used in Healthcare
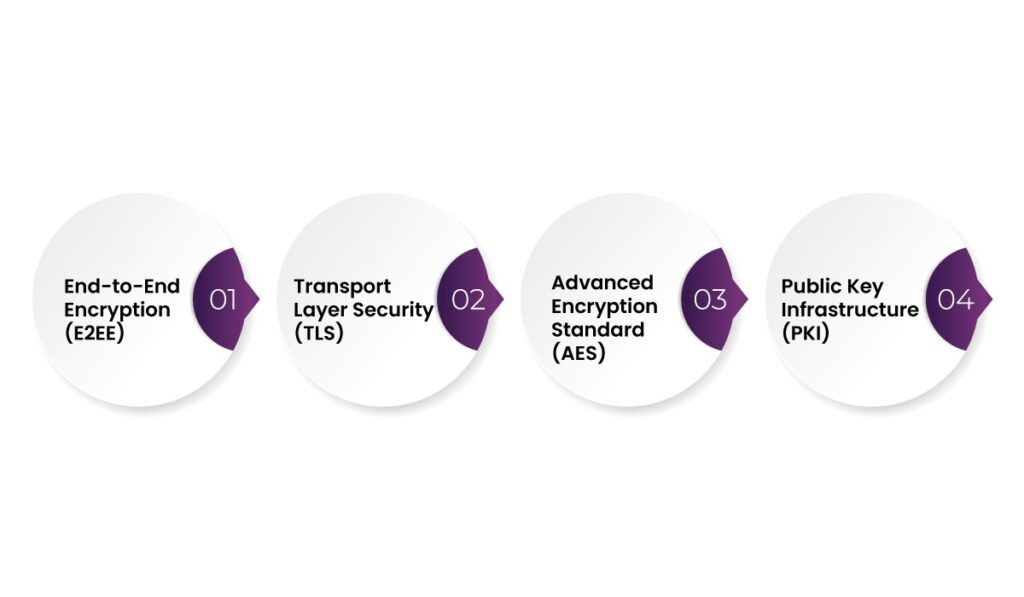
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) – Data is encrypted on the sender’s device and decrypted only by the intended recipient. This method prevents third parties, including service providers, from accessing the data.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) – TLS encrypts data while it is in transit over networks, such as when patients access their medical records via a web portal.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) – AES is widely used to encrypt stored data, so that patient records remain inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) – This system employs asymmetric encryption where a public key encrypts the data, and a private key is required to decrypt it, adding an extra layer of security.
Implementing Encryption in Healthcare Systems
To apply encryption effectively, organizations must integrate it across all communication channels, including:
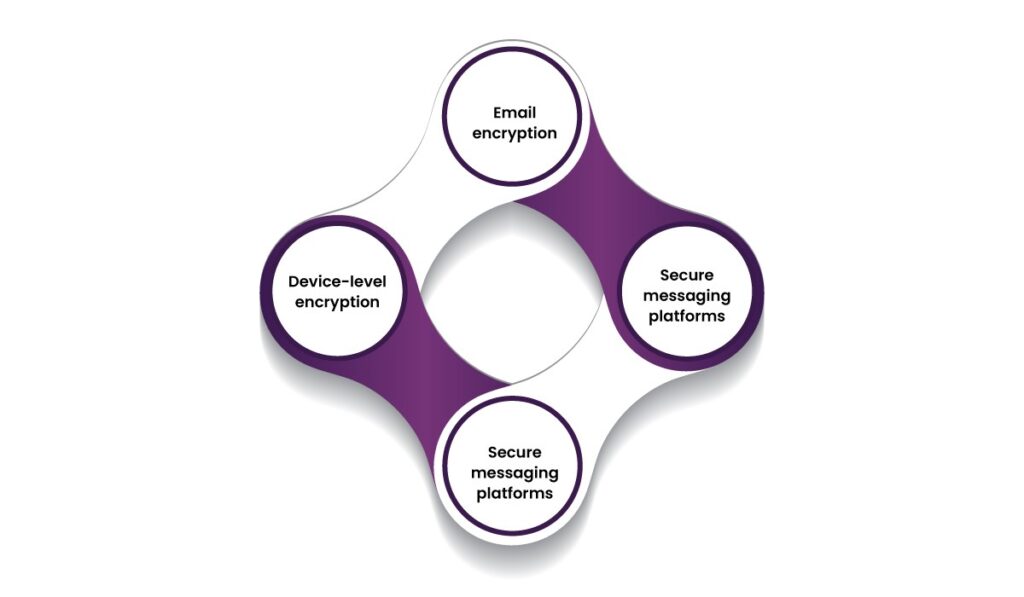
- Email encryption for transmitting patient records.
- Secure messaging platforms for internal communications between healthcare professionals.
- Encrypted cloud storage to safeguard backup data.
- Device-level encryption for mobile devices used by healthcare workers.
By implementing these measures, healthcare providers minimize the risk of data breaches, accidental leaks, and unauthorized access.
Navigating Compliance in Healthcare Data Security
Key Regulatory Frameworks Governing Healthcare Data Transfers
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have established stringent compliance standards to protect sensitive patient data. Healthcare providers must align with these regulations to maintain operational integrity and avoid legal repercussions.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – Enacted in the U.S., HIPAA mandates the protection of patient health information (PHI) during storage and transmission.
- The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) – Strengthens HIPAA by enforcing penalties for data breaches and encouraging the adoption of secure electronic health record (EHR) systems.
- ISO/IEC 27001 – A globally recognized framework that outlines best practices for information security management in healthcare.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – Applicable in the European Union, GDPR enforces strict data protection laws, requiring healthcare organizations to obtain explicit patient consent before processing data.
Steps to Achieve Regulatory Compliance
- Data Classification and Access Control – Identify sensitive data and restrict access based on user roles. For example, physicians may have full access, whereas administrative staff may only view non-medical information.
- Audit Trails and Monitoring – Logging every data transfer allows organizations to track potential breaches and detect suspicious activities in real-time.
- Patient Consent Management – Healthcare institutions must clearly inform patients about how their data will be used and obtain explicit consent before transferring information to third parties.
- Third-Party Security Assurance – Any vendor handling healthcare data, such as cloud service providers, must comply with relevant regulations to prevent liability issues.

Following these practices helps healthcare organizations align with legal standards while maintaining patient trust.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Secure Healthcare Data Transfers
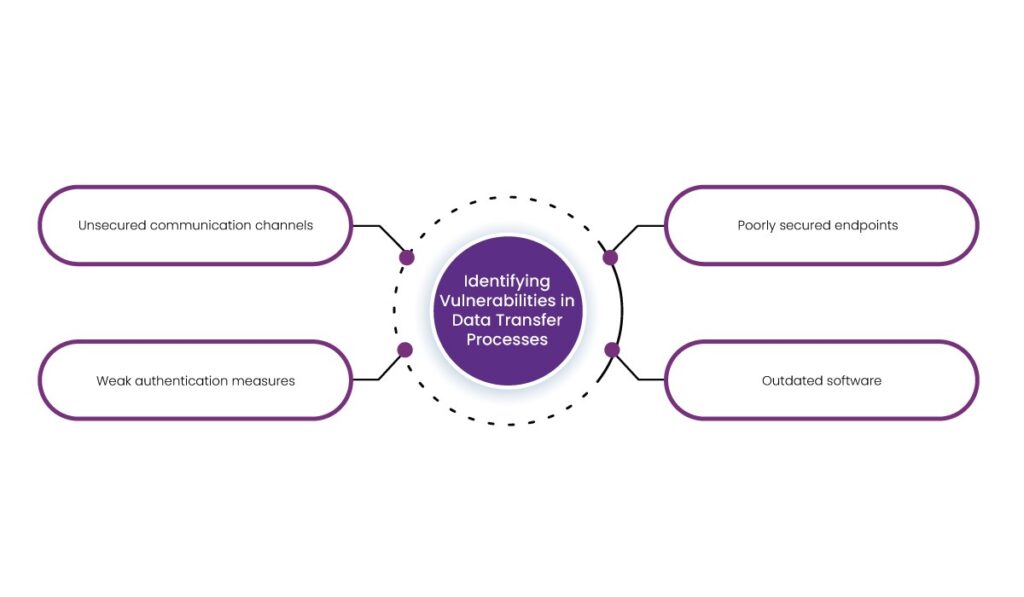
1. Identifying Vulnerabilities in Data Transfer Processes
The first step in risk mitigation is recognizing where threats exist. Common vulnerabilities include:
- Unsecured communication channels – Using standard email or non-encrypted messaging services exposes data to interception.
- Weak authentication measures – Login credentials alone are insufficient to protect access to sensitive records.
- Poorly secured endpoints – Laptops, smartphones, and tablets used by healthcare professionals can be exploited if not adequately protected.
- Outdated software – Systems without the latest security patches create entry points for cybercriminals.
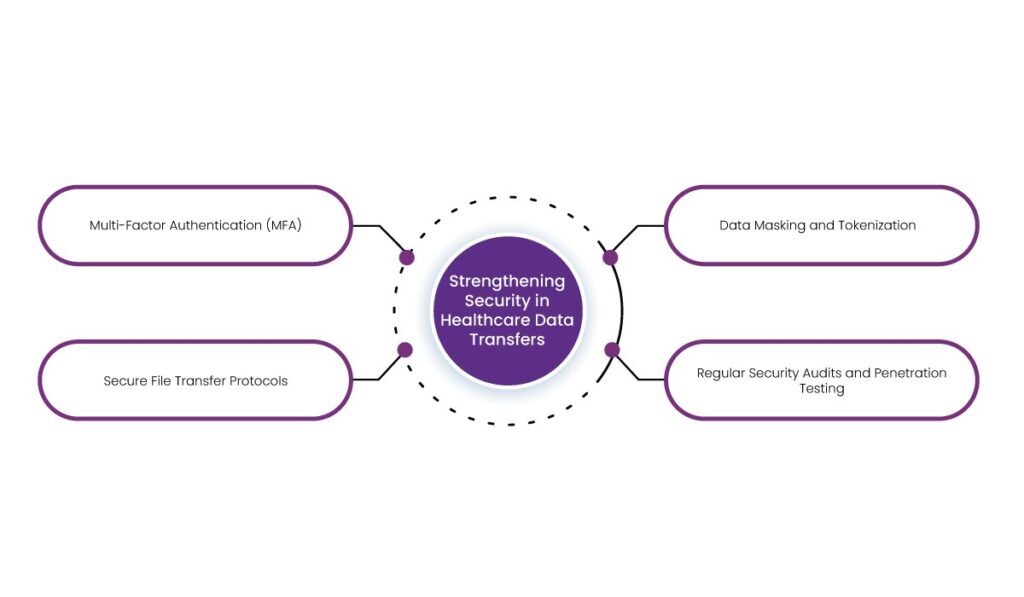
2. Strengthening Security in Healthcare Data Transfers
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding an extra authentication layer reduces unauthorized access risks. For example, requiring biometric authentication alongside a password for system access enhances security.
- Secure File Transfer Protocols – Implementing protocols like Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) ensures that data remains protected during transmission.
- Data Masking and Tokenization – Masking techniques replace sensitive patient details with non-sensitive equivalents, making intercepted data useless to unauthorized individuals.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing – Conducting frequent security assessments helps identify weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them.
How AERIS Secures Healthcare Data Transfers Without Compromising Security
AERIS, an Adaptive Exchange Interoperability System, makes data exchange effortless while prioritizing security, compliance, and scalability. Here’s how it works
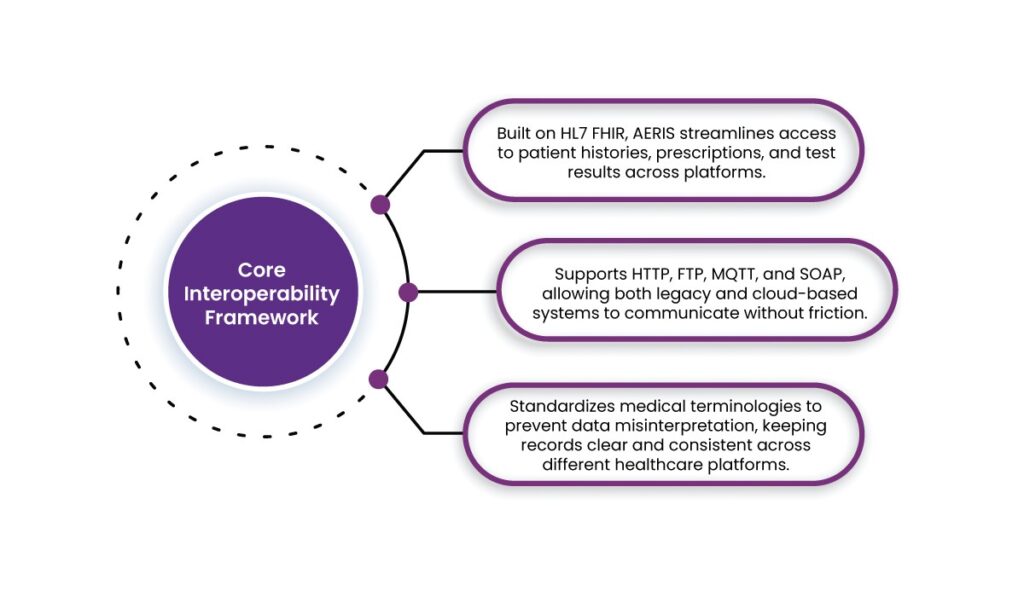
1. Core Interoperability Framework
- Built on HL7 FHIR, AERIS streamlines access to patient histories, prescriptions, and test results across platforms.
- Supports HTTP, FTP, MQTT, and SOAP, allowing both legacy and cloud-based systems to communicate without friction.
- Standardizes medical terminologies to prevent data misinterpretation, keeping records clear and consistent across different healthcare platforms.
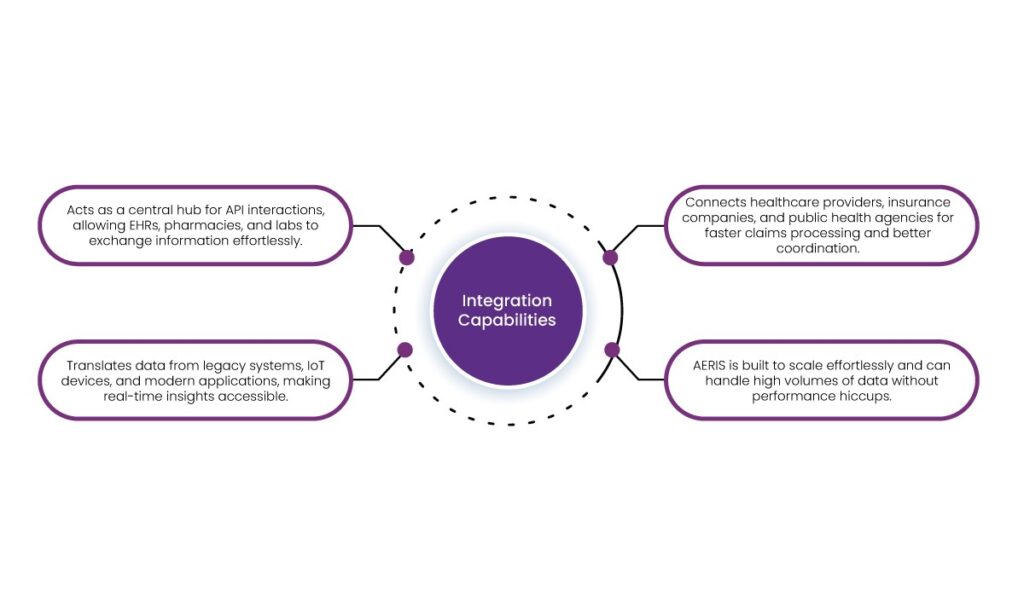
2. Integration Capabilities
- Acts as a central hub for API interactions, allowing EHRs, pharmacies, and labs to exchange information effortlessly.
- Translates data from legacy systems, IoT devices, and modern applications, making real-time insights accessible.
- Connects healthcare providers, insurance companies, and public health agencies for faster claims processing and better coordination.
- AERIS is built to scale effortlessly and can handle high volumes of data without performance hiccups.
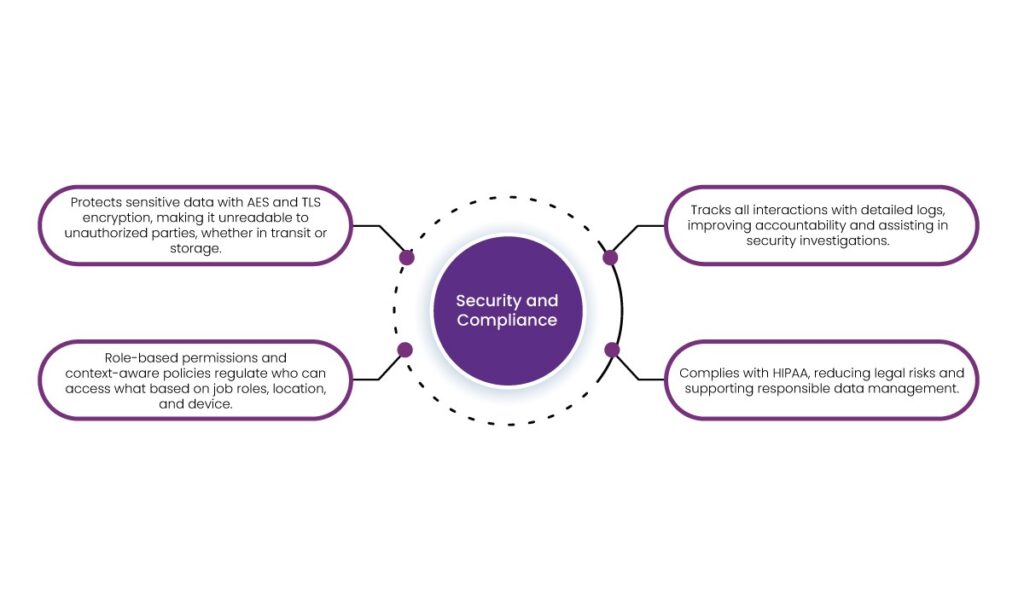
3. Security and Compliance
- Protects sensitive data with AES and TLS encryption, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties, whether in transit or storage.
- Role-based permissions and context-aware policies regulate who can access what based on job roles, location, and device.
- Tracks all interactions with detailed logs, improving accountability and assisting in security investigations.
- Complies with HIPAA, reducing legal risks and supporting responsible data management.
Final Thoughts
Securing healthcare data transfers requires a multi-layered approach that integrates encryption, regulatory compliance, and proactive risk mitigation.
AERIS simplifies this challenge by providing a secure, FHIR-based data exchange solution. With advanced encryption, compliance-driven architecture, and seamless integration capabilities, AERIS helps healthcare organizations safeguard patient information while optimizing data workflows. Discover how AERIS can enhance your healthcare data transfers—contact us today for a personalized demo.
FAQs
1. Why are healthcare data transfers a primary target for cybercriminals?
Healthcare records contain sensitive information like patient history, prescriptions, and insurance details, which can be exploited for identity theft and fraudulent activities. These records are more valuable on the black market than financial data.
2. How does encryption help secure healthcare data transfers?
Encryption converts sensitive information into an unreadable format, making it accessible only to authorized users. This prevents unauthorized access, even if data is intercepted during transmission.
3. How does AERIS improve healthcare data transfer security?
AERIS enhances security through AES and TLS encryption, role-based access controls, and detailed logging of all data interactions. It complies with key regulations like HIPAA to help organizations manage legal and security risks.
4. How can healthcare providers prevent unauthorized access to patient data?
Implementing access control measures such as role-based permissions, biometric authentication, and continuous monitoring helps restrict access to only authorized personnel.
5. Why should healthcare organizations consider AERIS for data security and compliance?
AERIS provides a scalable and compliant data exchange solution with built-in encryption, seamless integration with legacy and modern systems, and a structured approach to protecting sensitive patient data.













