Today, with digital health technologies like electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and AI-driven diagnostics becoming the norm, managing patient information effectively isn’t just an operational necessity—it directly impacts medical outcomes, regulatory compliance, and overall patient experience.
However, without a structured approach, data mismanagement can lead to inefficiencies, security risks, and fragmented care. From privacy concerns to interoperability hurdles, healthcare organizations face mounting challenges in optimizing their data strategies. In this blog, we will discuss the role of patient data management in healthcare governance, the obstacles that stand in the way, and how cutting-edge solutions like PULSE are reshaping the industry.
Table of Contents
The Role of Patient Data Management in Healthcare
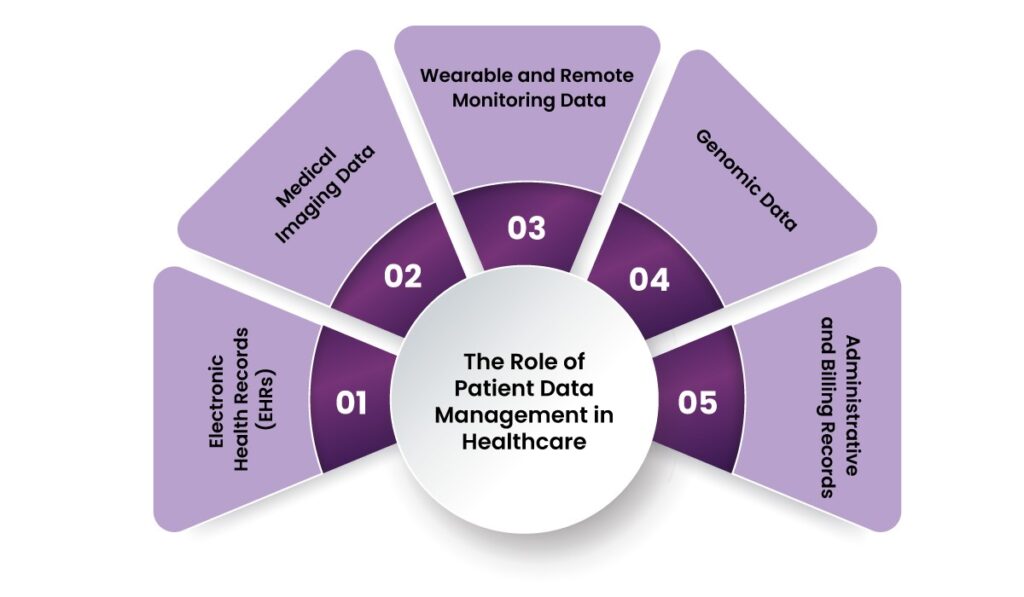
Patient data management involves collecting, storing, accessing, and analyzing patient information to improve clinical decision-making and operational efficiency. It goes beyond traditional record-keeping, integrating multiple data sources such as:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital versions of patient histories, treatment plans, and lab results.
- Medical Imaging Data: X-rays, MRIs, and other diagnostic images stored in Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS).
- Wearable and Remote Monitoring Data: Information from fitness trackers, glucose monitors, and remote sensors.
- Genomic Data: Personalized insights into patient predispositions and treatment responses.
- Administrative and Billing Records: Financial data on patient treatments and insurance claims.
Therefore, with vast amounts of healthcare data being generated daily, effective patient data management strategies are vital for maintaining accurate, up-to-date, and accessible records.
Challenges in Managing Patient Data
Despite the advantages, achieving patient data management presents several challenges. Some of the most pressing issues include:
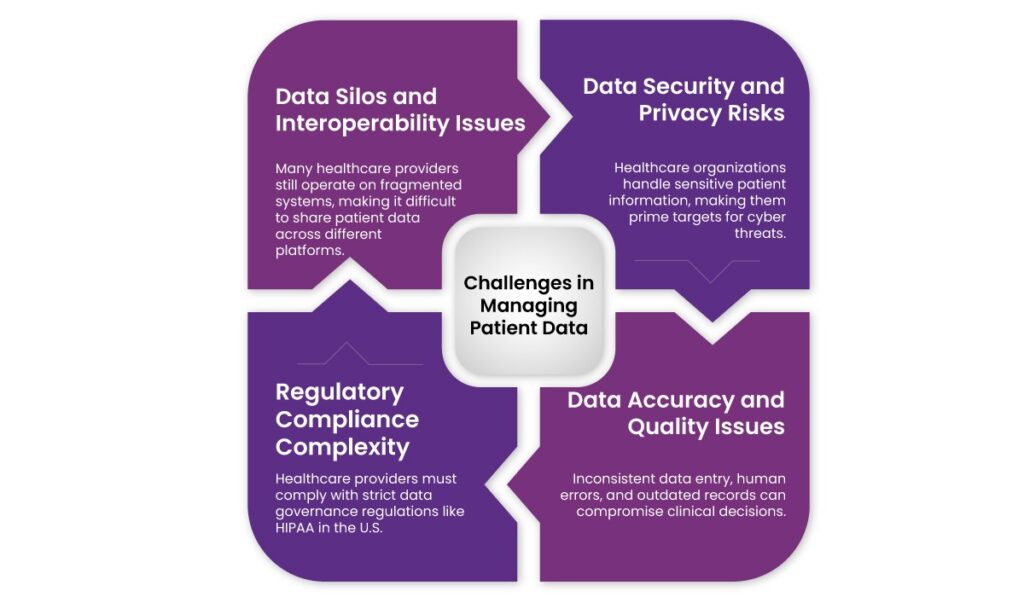
1. Data Silos and Interoperability Issues
Many healthcare providers still operate on fragmented systems, making it difficult to share patient data across different platforms. This lack of interoperability delays care coordination, resulting in duplicated tests and incomplete medical histories.
2. Data Security and Privacy Risks
Healthcare organizations handle sensitive patient information, making them prime targets for cyber threats. Therefore, ransomware attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access can lead to HIPAA violations and loss of patient trust.
3. Regulatory Compliance Complexity
Healthcare providers must comply with strict data governance regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. However, adhering to these evolving guidelines requires continuous adaptation.
4. Data Accuracy and Quality Issues
Inconsistent data entry, human errors, and outdated records can compromise clinical decisions. Therefore, reliable patient data management requires real-time updates, validation protocols, and automation to minimize errors.
How PULSE Helps Optimize Patient Data Management
Healthcare organizations must adopt solutions like PULSE to optimize patient data management to enhance security, accessibility, and overall efficiency. Here’s how PULSE helps implement effective patient data management:
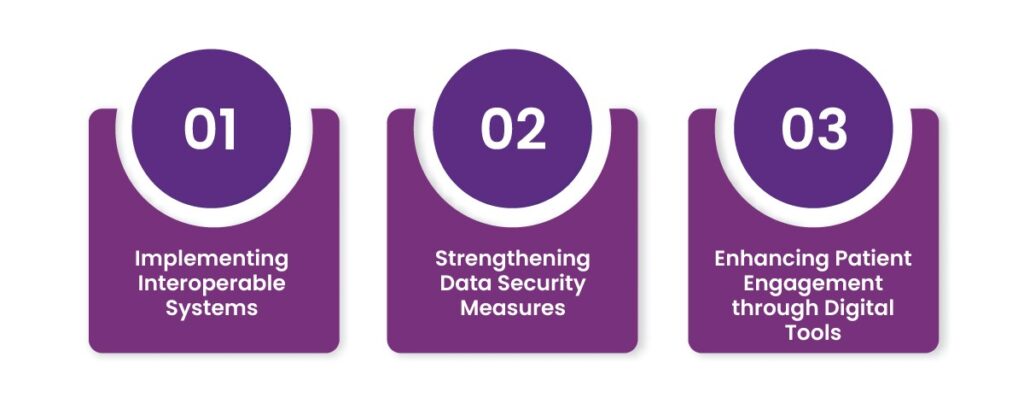
1. Implementing Interoperable Systems
Adopting industry standards such as HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) promotes seamless data exchange between EHR systems, labs, pharmacies, and insurance providers. Also, cloud-based platforms like PULSE blend centralized patient data management with decentralized access through Distributed Ledger Technology. This leads to faster diagnoses and smoother care transitions while empowering patients with full data control.
2. Strengthening Data Security Measures
Protecting patient data requires multi-layered security approaches. PULSE sets the benchmark with a multi-layered security infrastructure that safeguards sensitive healthcare information.
- Advanced Encryption for Data Protection
PULSE employs state-of-the-art encryption protocols to protect patient data during storage and transmission. By converting sensitive information into a secure, unreadable format, PULSE prevents unauthorized access and minimizes the risk of breaches.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs
With zero-knowledge proofs, PULSE verifies critical patient details—such as identity or insurance information—without exposing unnecessary personal data. This method enhances security while maintaining transparency, giving healthcare providers the reliable verification they need without compromising patient confidentiality.
- Intelligent Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
PULSE integrates a granular, role-based access control system that restricts data access based on user roles within a healthcare organization. This minimizes data exposure and allows:
- Doctors to access patient histories and prescriptions.
- Billing teams to handle financial data without viewing clinical records.
3. Enhancing Patient Engagement through Digital Tools
With PULSE, patients can access their health records, schedule appointments, receive real-time updates, and communicate directly with their healthcare providers through secure messaging. Its intuitive patient portal and mobile-friendly interface empower individuals to stay informed about their treatment plans, improving adherence and care coordination.
Therefore, by centralizing essential health data in one accessible platform, PULSE offers a more connected and efficient healthcare experience for both patients and providers.
Emerging Trends of Patient Data Management in Healthcare
The evolution of patient data management is shaping the future of personalized medicine and value-based healthcare. Emerging trends include:
1. Predictive Analytics for Preventive Care
AI-driven models can analyze patient data to predict potential health risks and facilitate early interventions. For example, predictive algorithms can identify patients at high risk for chronic diseases and suggest lifestyle modifications.
2. IoT-Enabled Remote Monitoring
Wearable devices and IoT sensors continuously collect patient vitals and feed real-time data into EHR systems. This can promote remote patient monitoring, reduce hospital readmissions and improve chronic disease management.
3. Ai-powered chatbots for Data Entry and Patient Support
AI-driven chatbots assist in collecting patient history, scheduling appointments, and offering symptom-based guidance. These tools enhance efficiency while reducing the workload on healthcare staff.
4. Advanced Data Governance Frameworks
To maintain compliance, healthcare organizations are adopting structured data governance frameworks that define roles, policies, and procedures for handling patient data. These frameworks support ethical AI use, consent management, and secure data sharing.

Final Words
Optimizing patient data management is fundamental to improving healthcare delivery, enhancing data governance, and fostering innovation. As healthcare continues its digital transformation, integrating AI, DLT, and interoperability standards will redefine how patient data is stored, accessed, and utilized.
By embracing robust patient data management strategies, healthcare providers can enhance clinical decision-making, safeguard patient privacy, and drive more efficient, personalized care. Discover how PULSE can help you take control of your patient data and drive better healthcare outcomes. Contact us today and get a free consultation!
FAQs
1. How does interoperability impact patient data management?
Lack of interoperability leads to fragmented systems, making it difficult to share patient information across healthcare providers. This can result in duplicated tests, incomplete medical histories, and delays in care coordination.
2. What measures can healthcare organizations take to protect patient data?
Healthcare organizations can enhance data security by implementing encryption protocols, role-based access controls, zero-knowledge proofs for secure verification, and adopting multi-layered security frameworks.
3. How does PULSE improve patient data management?
PULSE optimizes data management by implementing interoperable systems, strengthening security measures, enabling patient access to health records, and facilitating real-time communication between patients and healthcare providers.
4. What role do AI and predictive analytics play in patient data management?
AI-driven predictive models analyze patient data to identify potential health risks, allowing early intervention and personalized treatment plans to improve patient outcomes.
5. What are the emerging trends in patient data management?
Some emerging trends include AI-powered chatbots for patient support, predictive analytics for preventive care, IoT-enabled remote monitoring, and advanced data governance frameworks for ethical and secure data handling.
6. How does interoperability impact patient data management?
Lack of interoperability leads to fragmented systems, making it difficult to share patient information across healthcare providers. This can result in duplicated tests, incomplete medical histories, and delays in care coordination.














