In today’s competitive market, managing a product from idea to market success is a challenge. Research shows that nearly 30% of new products fail during the first two years of launch due to poor lifecycle management. Many businesses launch products without a clear strategy, leading to missed opportunities and inefficiencies. As a result, products often fail to reach their full potential.
The key to overcoming this challenge is understanding the product lifecycle process. With the right approach, businesses can manage each stage: development, growth, maturity, and decline effectively. This structured approach helps reduce risks, improve resource use, and lead to long-term success.
Let’s see the six stages of the product development process and the real-life success stories of the product lifecycle management.
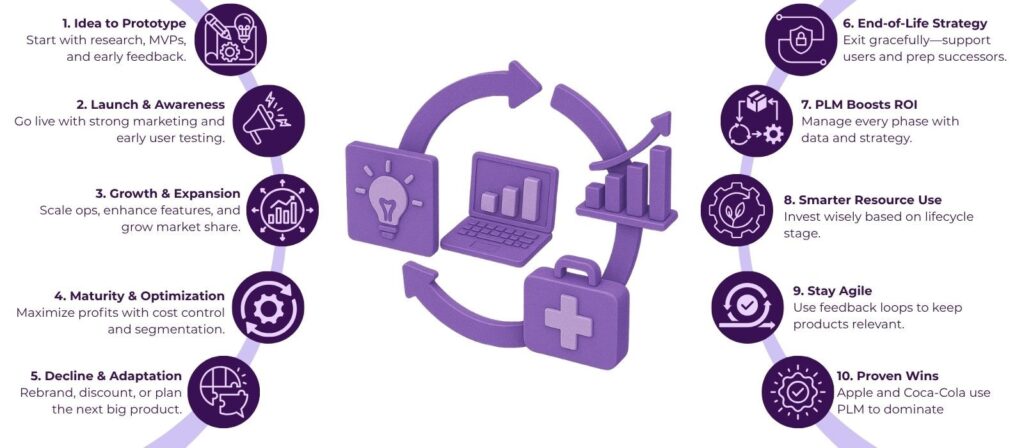
Table of Contents
Understand the Difference Between Product Lifecycle and Product Lifecycle Management Process
The product lifecycle process refers to the stages a product goes through from concept to end-of-life (EOL), including introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and eventual discontinuation. It helps businesses understand how products evolve in the market and the strategies needed at each phase.
In contrast, the product lifecycle management (PLM) process involves managing the product through its entire lifecycle using tools, strategies, and data. PLM focuses on optimizing each phase, such as design, production, and customer feedback, to reduce costs, improve quality, and align with business goals.
In short, the product lifecycle is the natural progression of a product, while PLM is the systematic management to ensure product success.
6 Stages of the Product Lifecycle Process
The Product Lifecycle Process consists of several stages, each of which plays a crucial role in guiding a product from conception to its eventual phase-out, ensuring it reaches its full market potential.
1. Concept/Development Stage
The first stage involves the ideation and feasibility analysis of a product. In this phase, businesses find market needs, perform concept testing, and analyze potential competitors. This stage includes developing a prototype and conducting early-stage design validation through customer feedback. It’s crucial to perform risk analysis and estimate costs, which forms the foundation for resource allocation in the subsequent stages.
Tips:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand customer needs and industry gaps.
- Use agile methodologies to refine and iterate the product concept quickly.
- Develop MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) to test and validate core features with a small audience.
2. Introduction Stage
Once the product is ready for launch, it enters the introduction phase, where the focus is on market penetration and awareness. During this stage, marketing strategies like targeted advertising and promotions are used to generate initial traction. Product distribution channels are expanded, and businesses often rely on early adopters for feedback to refine features and resolve any user experience (UX) issues.
Tips:
- Leverage digital marketing to build awareness and attract early adopters.
- Establish strategic partnerships for better market penetration and distribution.
- Monitor customer feedback closely to identify and fix any initial flaws or issues.
3. Growth Stage
As the product gains acceptance, the growth stage focuses on scaling operations. The sales curve starts to accelerate, and businesses work to expand their market share. This is the phase where the product undergoes differentiation through enhanced features or competitive pricing. Process optimization and supply chain scaling become key strategies for maximizing profitability and minimizing lead times.
Tips:
- Focus on scaling production and enhancing supply chain efficiency to meet demand.
- Invest in customer acquisition strategies through targeted marketing and promotions.
- Analyze the competitive landscape regularly and optimize your unique selling proposition (USP).
4. Maturity Stage
The product reaches its peak market share during the maturity phase, and growth starts to slow down. To maintain a competitive advantage, businesses focus on market segmentation and product line extension. Cost efficiency is a priority, and the product may undergo minor updates or improvements to extend its lifecycle. Companies may also explore brand loyalty programs to retain customers and fend off competitors.
Tips:
- Optimize pricing strategies to stay competitive while maintaining profitability.
- Expand your product portfolio or offer complementary products to maintain customer interest.
- Streamline operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency as the market stabilizes.
5. Decline Stage
During the decline stage, sales begin to decline due to market saturation, technological advancements, or shifting customer preferences. Companies may reduce their marketing spend or consider rebranding or updating their products. In some cases, the product may be discontinued or sold to third parties. Efficient management of inventory turnover and asset disposition becomes critical to minimize losses.
Tips:
- Monitor sales trends and decide whether to rejuvenate, discontinue, or replace the product.
- Offer discounts or special deals to clear remaining inventory and maximize remaining revenue.
- Start planning for the next innovation to maintain market relevance and focus on future opportunities.
6. End-of-Life Stage
The final stage of the product lifecycle is when the product is phased out completely. The end-of-life (EOL) process involves removing the product from the market, discontinuing production, and managing customer transition plans. In some cases, businesses may introduce a successor product to replace the old one, utilizing lessons learned throughout the product’s lifecycle to ensure smoother adoption and integration into the market.
Tips:
- Communicate proactively with customers about product discontinuation and alternatives.
- Offer support or replacement products for customers transitioning away from the old product.
- Analyze product performance data from all stages to learn valuable lessons for future product development.
Benefits of Product Lifecycle Management for Businesses
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) helps businesses optimize every stage of a product’s journey, from design to customer feedback , leads to efficiency and profitability
- Data-Driven Optimization: By analyzing KPIs at each lifecycle stage, businesses can make evidence-based decisions, improving product features and forecasting demand for better profitability and adoption.
- Resource Allocation Efficiency: Understanding lifecycle stages helps businesses allocate resources effectively, investing in high-return marketing during the introduction phase and minimizing costs during decline.
- Lifecycle Costing for Margin Improvement: Lifecycle costing identifies opportunities to reduce production, marketing, and distribution costs, optimizing profit margins, particularly in the maturity and decline phases.
- Agility in Innovation: Managing the lifecycle with agile methodologies allows businesses to quickly adapt to market feedback implementing updates or new features to maintain market relevance and customer satisfaction.
- Strategic Portfolio Management: The lifecycle process aids in portfolio optimization, helping businesses manage a mix of growth products and mature offerings, identifying gaps, and making strategic decisions to maximize profitability.
Real-Life Success Story of Product Lifecycle Process
The Product Lifecycle Process is essential for guiding a product from its initial concept to market success. Listed below are two success story of product lifecycle process.
1. Apple iPhone
Apple’s iPhone is a prime example of successful product lifecycle management. By consistently innovating with each new model, Apple has extended the maturity phase and maximized profitability. For example, the iPhone 12 saw a 25% increase in sales compared to its predecessor in the first quarter after launch, demonstrating Apple’s ability to maintain growth in the mature phase through regular updates and improvements.
The strategic introduction of new features, such as the A14 chip and 5G support, enabled Apple to continually differentiate the iPhone, extending its lifecycle and maintaining its position as a market leader for over a decade.
2. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola’s management of its flagship product is another success story in product lifecycle management. Coca-Cola consistently extends the maturity phase of its classic drink by introducing new packaging, flavor variations, and targeted marketing campaigns.
The company has successfully managed the lifecycle of its flagship product through market segmentation, targeting both health-conscious consumers with low-calorie options and younger generations through limited-edition flavors. In 2020, Coca-Cola’s total revenue reached $37.27 billion, showcasing its ability to maintain strong market presence and profitability even as the product approaches the end of its lifecycle.
Final Words:
Mastering the product lifecycle process is crucial for businesses seeking to remain competitive and achieve sustained long-term success. By effectively managing each stage, from ideation to end-of-life, companies can optimize resources, reduce risks, and maintain profitability. Whether you’re introducing a new product or managing an existing one, understanding and applying lifecycle strategies is key to sustained growth.
At Helixbeat, our product development services are designed to guide your products through every phase of the lifecycle. With our expertise in agile methodologies, data-driven decision-making, and innovative solutions, we help businesses optimize their product’s journey from concept to market domination.
Let us help you turn your product ideas into lasting market successes. Book a free consultation with us today.
FAQ:
1. Example for Product Life Cycle?
The iPhone is a great example. It went through stages from concept development, introduction, growth, and maturity and continues with updates to extend its lifecycle and maintain market relevance.
2. What is the Full Product Lifecycle?
The full product lifecycle covers the entire journey of a product from concept through development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline until it reaches end-of-life (EOL).
3. What are the 5 Phases of Product Lifecycle?
- Introduction: Launch phase, focusing on awareness.
- Growth: Sales rise as the product gains acceptance.
- Maturity: Sales stabilize at peak levels.
- Decline: Sales decline due to saturation or competition.
- End-of-Life: The product is discontinued or replaced.
4. What is the Agile Life Cycle?
The Agile lifecycle involves iterative development in short sprints, with regular feedback, allowing teams to adapt to changing requirements and continuously improve the product.
5. What is PDLC vs SDLC?
- PDLC (Product Development Life Cycle) focuses on the stages from concept to market for physical or digital products.
- SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) is specific to the design, development, testing, and deployment of software applications.














