How certain are you that your hospital is doing everything it should to protect patient data? With ransomware attacks, data leaks, and regulatory penalties on the rise, safeguarding sensitive health information is no longer optional; it’s mission critical.
From medical histories and test results to insurance details and contact information, every bite of patient data is a potential target if not adequately protected.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything your practice needs to know about patient data security including shared threats, best practices, legal requirements, and how media like PULSE by Helixbeat helps modern clinics stay secure, compliant, and trusted. Whether you’re managing a small setup or a multi-specialty chain, this guide will help you reduce risk while delivering care with confidence.
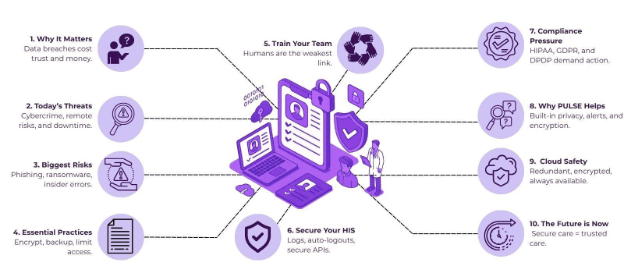
Table of Contents
What Is Patient Data Security and Why Does It Matter?
Patient data security guides encompass the systems, policies, and technologies used to protect sensitive patient information, including medical history, diagnostic reports, prescriptions, insurance records, and personal details, from unauthorized access, loss, or misuse. This contains both digital (EHRs, emails, cloud backups) and physical (printed records, consent forms) data.
In standard healthcare, where electronic health records and telemedicine have become the norm, the volume of data shared across various platforms has increased significantly. While this has improved efficiency and accessibility, it has also increased the risk of cyberattacks, accidental leaks, and privacy violations.
Why it matters:
- Protects patient trust and clinic reputation
- Avoids costly fines under regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and India’s DPDP Act
- Prevents identity theft and insurance fraud
- Enables secure data sharing among providers for better outcomes
- Forms the foundation of ethical, responsible digital care delivery
Why Data Security in Healthcare Is a Top Priority Today?
Healthcare organizations manage some of the most sensitive and high-value data in existence: patient health records, insurance details, prescriptions, diagnostics, and even biometric data. Unlike financial data, which can be altered or reset, a patient’s medical history is extensive, and once disclosed, it cannot be undone.
The risks of poor data security in healthcare are substantial:
- Data Breaches & Cyberattacks
- Healthcare is one of the top targets for cybercriminals. IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach report noted that the average breach in healthcare costs over $10 million, making it the most expensive industry for breaches.
- Ransomware attacks can cripple hospital operations, delay treatments, and compromise patient safety.
- Regulatory Penalties & Legal Liabilities
- Failing to comply with data protection laws, such as HIPAA, can result in substantial fines, license suspensions, or even legal action.
- Non-compliance not only damages the balance sheet but also erodes public trust and your brand’s reputation.
- Loss of Patient Trust
- A single incident of exposed health information can erode years of trust and confidence.
- Patients are increasingly aware of how their data is used and demand transparency and control over it.
- Operational Disruptions
- Security incidents frequently result in data loss, service downtime, and system lockouts, which can stall clinical operations, delay patient care, and increase administrative burdens.
- Increased Risk with Remote Tools
- As practices adopt telehealth, cloud platforms, and wearable integrations, the attack surface expands—making proactive data security essential, not optional.
- Strong data security in healthcare is not just about compliance—it’s about protecting lives, maintaining trust, and building a resilient digital practice.
CTA: Want to know how PULSE by Helixbeat helps safeguard patient records? [Book your personalized demo now].
Key Threats to Healthcare Information Security
Healthcare organizations, whether small clinics or large hospital networks are high-value targets for cybercriminals due to the firm’s often inflexible nature of medical data.
Here are the most critical threats to healthcare information security:
- Internal Threats (Human Error or Malicious Intent)
- Not all threats come from outside. In many cases, staff members unintentionally expose patient data through weak passwords, mishandling of records, or sharing of information over unsecured channels. Worse, disgruntled employees may deliberately access or leak sensitive data.
- Solution: Enforce strict role-based access controls, monitor activity logs, and conduct regular staff training.
- Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
- Fake emails or messages that appear legitimate can trick staff into revealing login credentials or clicking on malicious links. These attacks can lead to unauthorized access to the system and major data breaches.
- Solution: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), email filters, and phishing awareness programs to reduce risk.
- Ransomware Attacks
- Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts your data and demands payment for its release. In healthcare, this can paralyze entire systems—delaying diagnoses, canceling appointments, and compromising patient data security.
- Solution: Regularly back up data to secure locations and use endpoint protection to detect threats early.
- Third-Party Application Vulnerabilities
- Many clinics use third-party software tools for billing, scheduling, or telehealth—each of which could be a weak point if not properly secured. A breach in one tool can cascade across connected systems.
- Solution: Vet third-party vendors thoroughly, enforce API-level security, and restrict unnecessary data sharing.
Which Practices Are Essential for Patient Data Protection?
The answer isn’t just one—it’s a combination of proven strategies that work together to create a secure, compliant, and patient-trusted environment.
Here are the essential practices every healthcare provider must implement to safeguard patient data:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Not everyone on your staff needs access to everything. Role-based access ensures that team members only see the data required for their work. For example, front desk staff can schedule appointments without accessing medical histories, while doctors have full clinical access.
- Prevents internal misuse
- Reduces exposure during cyber incidents
- End-to-End Encryption
- All patient data, whether stored or in transit, should be encrypted. This makes it unreadable to unauthorized users, even in the event of a breach.
- Encrypt EHRs, email communications, and lab results
- Utilize HTTPS, VPNs, and encrypted backups to add an extra layer of protection.
- Regular Data Backup
- Daily or real-time backups can be the difference between a quick recovery and permanent data loss.
- Store backups offsite or on cloud platforms with disaster recovery protocols in place.
- Enables business continuity in case of ransomware or system failure.
- Should be tested periodically for integrity and accessibility.
- Ongoing Staff Training and Awareness
- Human error is often the weakest link in healthcare data security.
- Conduct regular training sessions on topics like phishing, password hygiene, and secure device usage.
- Helps staff recognize threats before they cause harm
- Fosters a culture of shared responsibility for data protection
What Security Measures Should Be Built into a HIS?
A Hospital Information System (HIS) serves as the digital backbone of modern healthcare operations, housing sensitive patient data, medical histories, laboratory results, prescriptions, and billing information.
So, what security measures are essential for protecting patient data within a HIS? Let’s explore the must-have features every HIS should incorporate:
- Comprehensive Audit Trails
- Every login, data access, edit, or deletion should be recorded in a time-stamped audit log.
- These logs help identify misuse, unauthorized access attempts, or internal errors and are essential for compliance with HIPAA and other healthcare regulations.
- Auto Logout and Session Management
- Idle sessions should automatically expire after a set time to prevent misuse from unattended terminals.
- Admins should also be able to remotely log out users and manage active sessions across devices.
- Secure API Integrations
- HIS platforms often integrate with labs, pharmacies, billing systems, and third-party diagnostic tools.
- APIs used in these connections must utilize token-based authentication, rate limiting, and encryption protocols (such as TLS/SSL) to prevent data interception or tampering.
How PULSE by Helixbeat Helps You Strengthen Patient Data Security?
Patient data breaches are not only costly; they can permanently damage trust and confidence. PULSE by Helixbeat is designed with privacy and security at its core, helping practices produce connected, compliant care without compromising security.
Here’s how PULSE supports airtight patient data security at every touchpoint:
- HIPAA-Grade Communication Tools
- Built-in WhatsApp, SMS, and email workflows are developed with privacy in mind.
- No sensitive knowledge is revealed, and all patient communications are encrypted.
- Secure Cloud Hosting and Backup
- PULSE is hosted on compliant, cloud-native infrastructure with built-in disaster recovery and redundancy.
- Even during downtime or cyber threats, your patient’s data remains safe and accessible.
- End-to-End Encryption
- Whether data is being entered, stored, or transmitted, PULSE applies complete encryption protocols.
- Patient records, appointment data, and communications are secure both in transit and at rest.
- Real-Time Alerts and Activity Logs
- Every login, data edit, or export is tracked in detailed audit logs.
- PULSE sends real-time alerts for suspicious behavior, failed login attempts, or access outside working hours.
To Sum It Up
Imagine this: A patient books an appointment for midnight. Their vitals are monitored through wearables. Follow-ups happen over WhatsApp. The care plan is personalized, proactive, and powered by real-time data. That’s not futuristic fiction; it’s the new reality shaped by digital health technology.
The clinics and hospitals that embrace it today aren’t just improving efficiency; they’re redefining what excellent healthcare feels like. And platforms like PULSE by Helixbeat are driving that change easier, faster, and brighter than ever before.
CTA: Interested in booking a PULSE demo now and experiencing firsthand how digital health technology can turn your clinic into a connected, patient-first powerhouse?
FAQs
What is patient data security in healthcare?
Patient data security refers to the systems, technologies, and practices that protect sensitive patient information—like medical history, test results, and contact details—from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse.
Why is data security in healthcare more critical today than it was before?
With increased digitization, telemedicine, and online data sharing, healthcare organizations face more cyber threats than ever. Breaches can lead to legal fines, reputation loss, and patient distrust.
What are the most common threats to healthcare data security?
Phishing attacks, weak passwords, unencrypted communication, unauthorized access, and insecure third-party integrations are among the top risks.
How can we keep patient data secure in our clinic?
Use encrypted communication, apply multi-factor authentication (MFA), train staff on data protocols, conduct regular audits, and implement access control.
Which of the following practices is important for data security?
All the following: using encrypted systems, keeping software updated, enabling audit trails, and restricting access based on user roles.
What security measures are essential for protecting patient data within a HIS (Hospital Information System?
HIS systems should include role-based access, automatic logout, audit logs, encryption at rest and in transit, and regular security patches.
How does PULSE by Helixbeat support patient data security?
PULSE offers smart access controls, encrypted communications, real-time alerts, secure cloud hosting, and full audit trails—making your clinic compliant and protected.
Can small clinics implement strong healthcare information security without large IT teams?
Yes. Tools like PULSE are cloud-based, user-friendly, and scalable for smaller setups—offering enterprise-grade security without complexity.
Is cloud storage safe for storing patient health records?
Yes, if it’s HIPAA/GDPR compliant and uses encryption, secure APIs, and role-based access—like PULSE’s cloud infrastructure.
What should we do first to improve patient data security?
Start with a digital audit. Identify your system vulnerabilities, train your team, and adopt a secure, all-in-one platform like PULSE to manage patient data safely.














