Today, healthcare is not just about providing timely care; it’s also about managing and sharing data securely and efficiently. But what happens when healthcare organizations fall behind on interoperability standards? The answer is simple: non-compliance can cost more than compliance ever will—in fines, lost reputation, operational inefficiencies, and even patient lives.
With regulators pushing for connected systems through mandates like the 21st Century Cures Act and HIPAA, the pressure is on healthcare providers, payers, and technology vendors to adapt. Unfortunately, many still underestimate the real cost of ignoring interoperability requirements. In this blog, we’ll break down how skipping out on healthcare interoperability solutions can turn into a financial and operational nightmare.
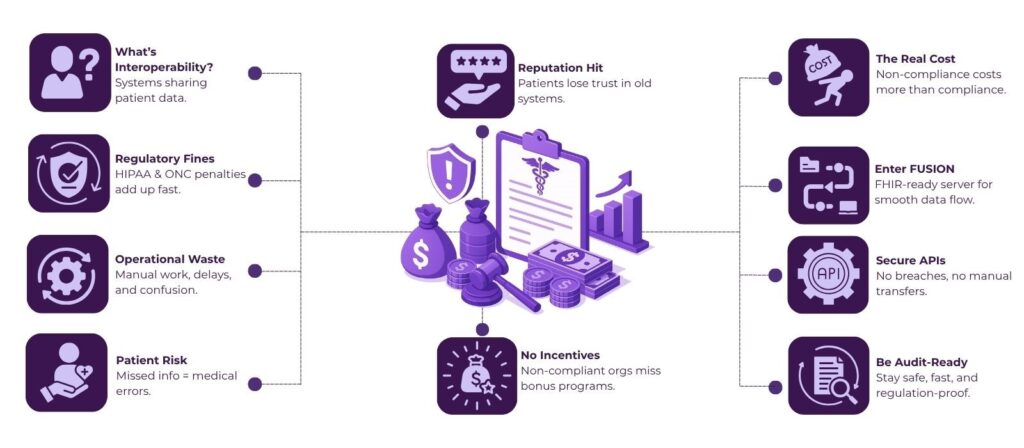
Table of Contents
What Is Healthcare Interoperability?
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of different health information systems, devices, and software applications to access, exchange, integrate, and use data in a coordinated manner. It plays a key role in improving patient outcomes, reducing errors, and speeding up care delivery.
There are several layers to interoperability:
- Foundational: The basic ability to transmit and receive data.
- Structural: Standardized data formats like HL7, FHIR, DICOM.
- Semantic: Consistent meaning of shared data using codes like SNOMED, LOINC.
- Organizational: Policies, workflows, and legal frameworks supporting seamless exchange.
The Real Costs of Ignoring Interoperability
1. Regulatory Fines and Penalties
Non-compliance doesn’t come cheap. For example:
- HIPAA violations can result in penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million.
- The Office of the National Coordinator (ONC) can also penalize EHR vendors and healthcare providers for information blocking, with fines of up to $1 million per instance.
- CMS can withhold Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements from non-compliant organizations.
These are not theoretical risks—many providers have already paid the price. For example, in 2021, Sharp HealthCare in California paid $70,000 to the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR) to settle a HIPAA violation after failing to provide timely access to patient records.
2. Operational Inefficiency and Data Silos
Without proper interoperability, care coordination becomes a mess. Staff spend countless hours manually transferring records, interpreting inconsistent data, and dealing with system mismatches. The result?
- Delayed diagnoses and treatment.
- Duplicated tests and procedures.
- Increased administrative burden.
According to a study by the American Hospital Association, hospitals lose nearly $1 million per year per facility due to interoperability-related inefficiencies.
3. Patient Safety Risks
Non-compliance isn’t just about money—it’s about lives. When systems can’t talk to each other:
- Allergies, medications, and past diagnoses may be missed.
- Emergency departments may operate blindly.
- Chronic care patients may receive disjointed treatment.
A 2016 Johns Hopkins study identified medical errors as the third leading cause of death in the U.S. While the study didn’t specifically name lack of data access, experts widely acknowledge that poor interoperability and fragmented health records contribute significantly to such errors.
4. Loss of Reputation and Trust
Patients today expect their data to move with them. They want access via mobile apps, online portals, and to receive care without repeating their medical history over and over again.
Organizations that fall short risk:
- Negative reviews on public platforms.
- Lower patient retention.
- Brand damage that affects growth.
In a competitive healthcare landscape, being perceived as outdated or inefficient can drive patients toward more modern, tech-savvy providers.
5. Lack of Eligibility for Incentives and Partnerships
Healthcare systems that adopt healthcare interoperability solutions can take advantage of incentive programs, grants, and federal initiatives. Those who don’t are left behind.
For example:
- CMS Promoting Interoperability Programs reward hospitals that meet data sharing and EHR standards.
- Value-Based Care models depend on real-time data exchange between providers and payers.
Failure to participate in these programs is like leaving free money on the table—and often, millions of dollars over time.
How FUSION Minimizes Risk in a Non-Compliant Healthcare Environment
When regulatory pressure around healthcare interoperability intensifies, the last thing your organization can afford is uncertainty. That’s where healthcare interoperability solutions like FUSION step in.
FUSION is a FHIR server built using RESTful APIs that stores patient data in the FHIR format, designed specifically to help healthcare providers, payers, and healthtech vendors meet interoperability mandates with confidence.
Here’s how FUSION minimizes compliance and operational risk:
- Built on FHIR Standards: FUSION uses HL7 FHIR structures to store and exchange patient data, aligning directly with the interoperability requirements set by the 21st Century Cures Act, TEFCA, and CMS. This reduces the risk of fines and penalties due to non-compliance.
- Secure RESTful APIs for Seamless Integration: With FUSION, you avoid clunky, error-prone integrations. Its RESTful API architecture allows secure, real-time data exchange with EHRs, labs, mobile apps, and payer systems—no manual transfers, no delays, no breaches.
- Eliminates Data Silos: FUSION centralizes patient information using standardized FHIR resources, making it easy to access, share, and update critical data across care teams—minimizing medical errors, duplicate testing, and treatment delays.
- Audit-Ready Infrastructure: From access logs to role-based controls, FUSION supports traceability and governance, helping your IT and compliance teams stay ahead of regulatory audits without added overhead.
In a healthcare landscape where the cost of non-compliance can spiral into the millions, FUSION offers a future-proof path to compliant, coordinated, and secure care delivery.
Final Thoughts
Staying compliant with interoperability regulations is not just a legal checkbox—it’s a strategic advantage. From improving patient safety to reducing operational waste, modern healthcare interoperability solutions pay for themselves many times over.
The cost of non-compliance isn’t just measured in fines. It reflects lost time, trust, talent, and opportunity.
FUSION helps you avoid those risks with a plug-and-play FHIR server built for real-world healthcare demands. From secure RESTful APIs to fully compliant FHIR data storage, it’s everything you need to stay aligned with evolving regulations. Contact us today and take the first step toward safer, smarter data exchange.
FAQs
1. Why are healthcare interoperability solutions important for compliance?
Healthcare interoperability solutions like FUSION support compliance with federal regulations like HIPAA, the 21st Century Cures Act, and CMS interoperability rules by enabling structured, standardized, and secure data sharing across systems.
2. How can healthcare interoperability solutions reduce the cost of non-compliance?
By aligning with legal and technical standards, healthcare interoperability solutions help organizations avoid regulatory fines, reduce operational inefficiencies, and minimize patient safety risks—thereby preventing costly mistakes and penalties.
3. Are healthcare interoperability solutions suitable for small practices?
Yes. Many healthcare interoperability solutions like FUSION are now cloud-based and scalable, offering cost-effective options for small clinics, rural hospitals, and individual practices without requiring major infrastructure upgrades.
4. What role does FHIR play in healthcare interoperability solutions?
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a data standard widely adopted by healthcare interoperability solutions to structure and exchange electronic health data in a consistent format. It enables faster integration between systems and applications.
5. What’s the difference between integration and interoperability in healthcare?
Integration connects systems; interoperability—especially through healthcare interoperability solutions—goes further by making the exchanged data understandable, usable, and consistent across platforms and providers.














